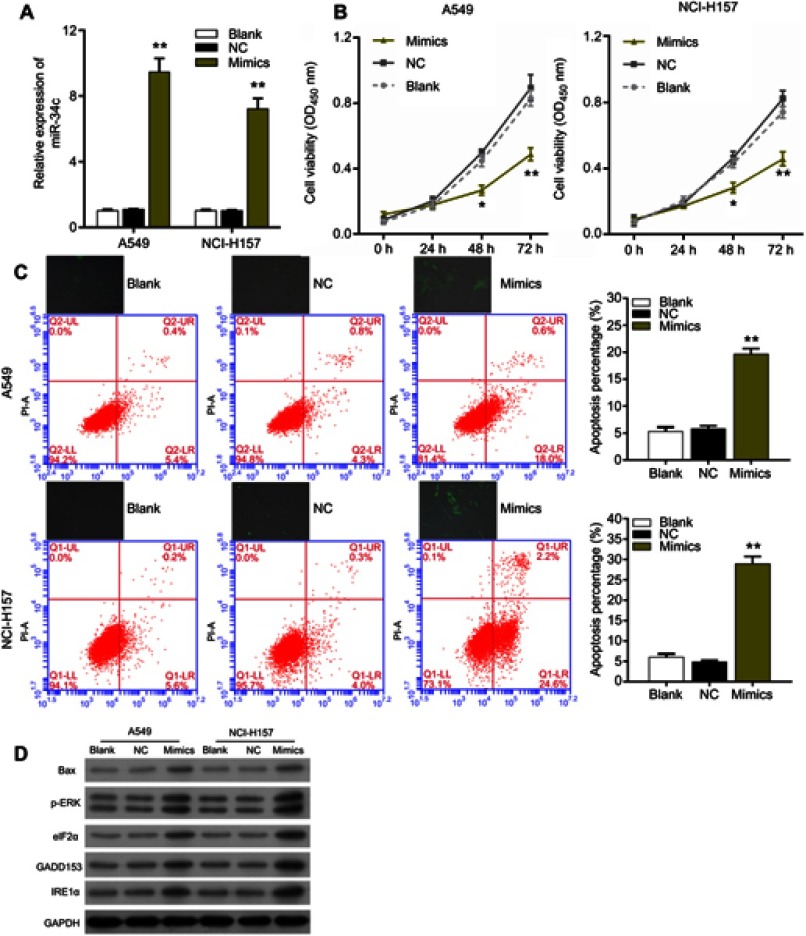
Figure 2.
miR-34c overexpression significantly inhibited proliferation, promoted apoptosis and induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in non-small cell lung cancer cells. (A) The relative levels of miR-34c expression in A549 and NCI-H157 cells transfected with nothing (blank control), the miR-34c negative control (NC), and miR-34c mimics were measured by qRT-PCR assays, **P<0.01 vs NC group. (B) Effects of miR-34c on the proliferation of A549 and NCI-H157 cells were evaluated via the CCK-8 assay, *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs NC group. (C) upper panel: cellular reactive oxygen species production was detected in A549 and NCI-H157 cells transfected with nothing, miR-34c, the NC or miR-34c mimics. Lower panel: flow cytometry analyses were performed to assess the apoptosis rates of A549 and NCI-H157 cells transfected with nothing, miR-34c, the NC or miR-34c mimics, **P<0.01 vs NC group. (D) The levels of Bax, p-ERK, eIF2α, GADD153, and IRE1α in miR-34c-treated A549 and NCI-H157 cells were examined via Western blot assays.