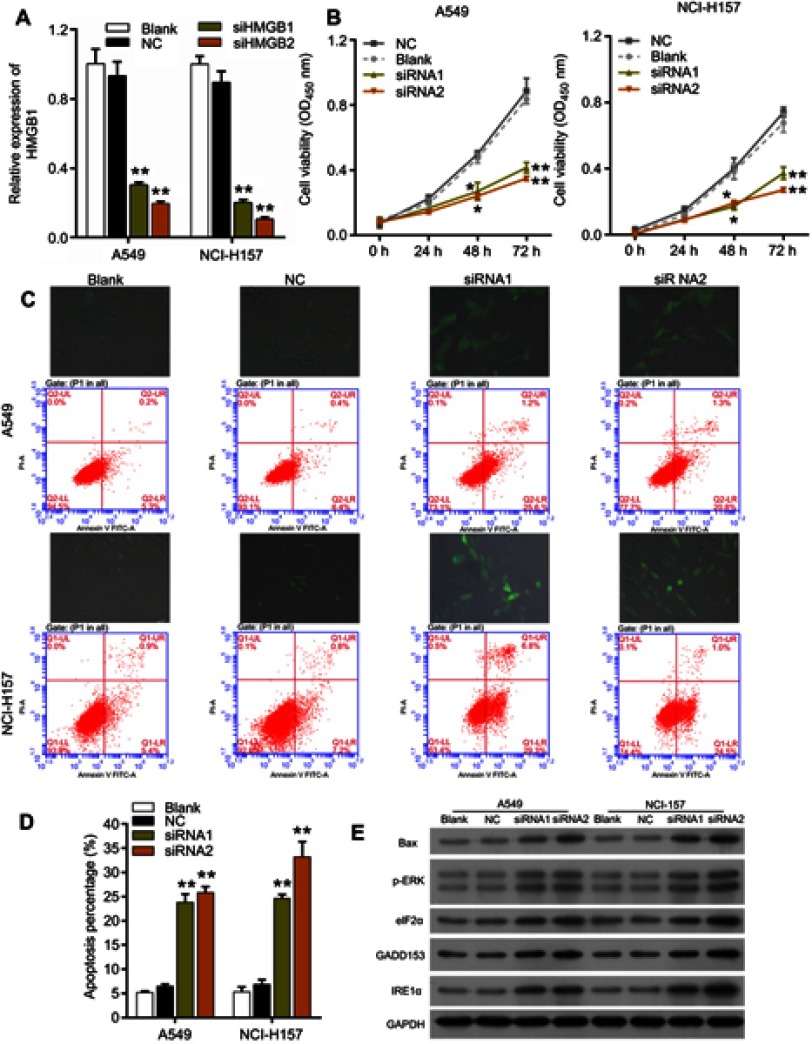
Figure 4.
Knockdown of HMGB1 strongly inhibited proliferation and promoted apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum stress in non-small cell lung cancer cells. (A) The knockdown efficiencies of two siRNAs targeting HMGB1 (si-HMGB1-1 and si-HMGB1-2) in A549 and NCI-H157 cells were assessed via the qRT-PCR assay, **P<0.01 vs NC group. (B) The effect of treatment with si-HMGB1-1 and si-HMGB1-2 on the proliferation of A549 and NCI-H157 cells was evaluated via the CCK-8 assay, **P<0.01 vs NC group. (C and D) Upper panel: the effects of HMGB1 knockdown on cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in A549 and NCI-H157 cells transfected with nothing, the NC or si-HMGB1-1 and si-HMGB1-2 were analyzed by using a ROS kit. Lower panel: the apoptosis rates of A549 and NCI-H157 cells transfected with nothing, the NC or si-HMGB1-1 and si-HMGB1-2 were detected by flow cytometric analysis (D), **P<0.01 vs NC group. (E) Western blot analysis of Bax, p-ERK, eIF2α, GADD153, and IRE1α expression in HMGB1-blocked A549 and NCI-157 cells.