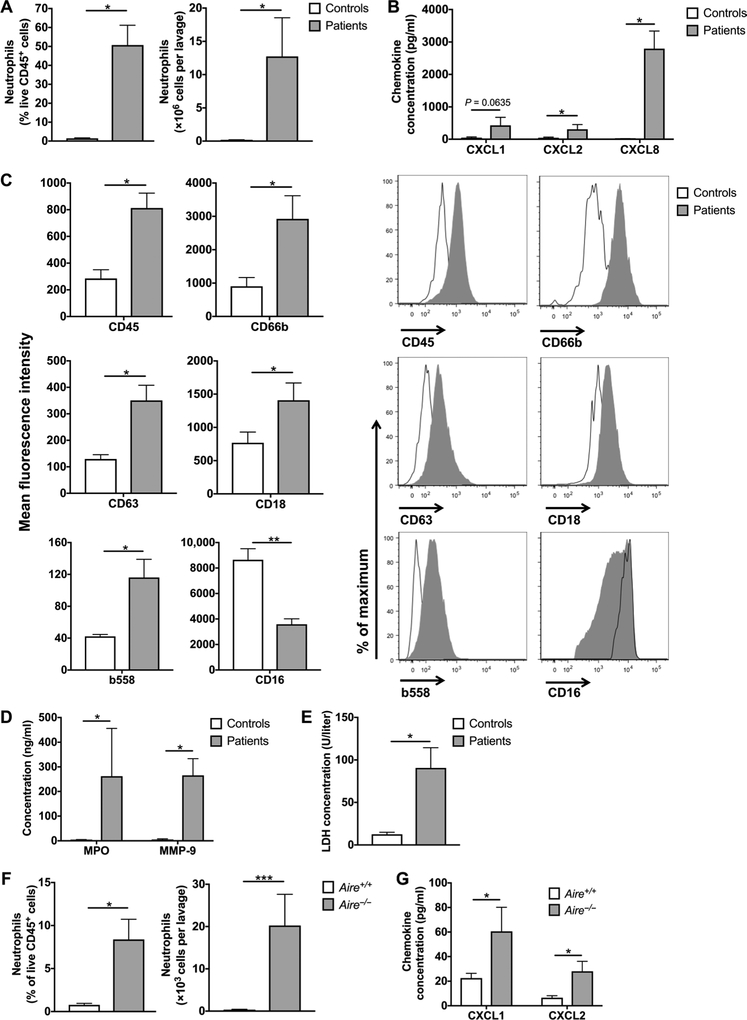
Fig. 3. Accumulation of activated neutrophils in the airways of patients with APECED pneumonitis.
(A) Neutrophils in the BAL of patients with APECED with pneumonitis (n = 5) and healthy controls (n = 4). Percentage of neutrophils within total CD45+ leukocytes (left) and total number of neutrophils per lavage (right). (B) Concentration of CXC neutrophil-targeted chemokines in the BAL of patients with APECED with pneumonitis (n = 5) and healthy controls (n = 4). (C) Neutrophil activation phenotype in BAL of patients with APECED with pneumonitis (n = 4 to 5) and healthy controls (n = 4). Shown are summary data (left) on mean fluorescence intensity and representative fluorescence-activated cell sorting histograms (right) for CD45, CD66b, CD63, CD18, b558, and CD16. (D) Concentration of the neutrophil products MPO and MMP-9 in the BAL of patients with APECED with pneumonitis (n = 5) and healthy controls (n = 4). (E) LDH concentration in the BAL of patients with APECED with pneumonitis (n = 5) and healthy controls (n=4). (F) Neutrophils in the BAL of Aire+/+ and Aire−/− mice (n = 8 to 10 per group; three independent experiments). Percentage of neutrophils within total CD45+ leukocytes (left) and total number of neutrophils per lavage (right). (G) Concentration of the CXC neutrophil-targeted chemokines CXCL1 and CXCL2 in the BAL of Aire+/+ and Aire−/− mice (n = 7 to 10 per group; three independent experiments). Differences between groups in all panels were determined using Mann-Whitney test with the exception of the differences between groups in the left panel of (F) (% of neutrophils within total CD45+ leukocytes) and on the right side of the graph in (G) (CXCL2 concentration), which were determined using unpaired t test with Welch’s correction. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***p< 0.001. All quantitative data represent means ± SEM.