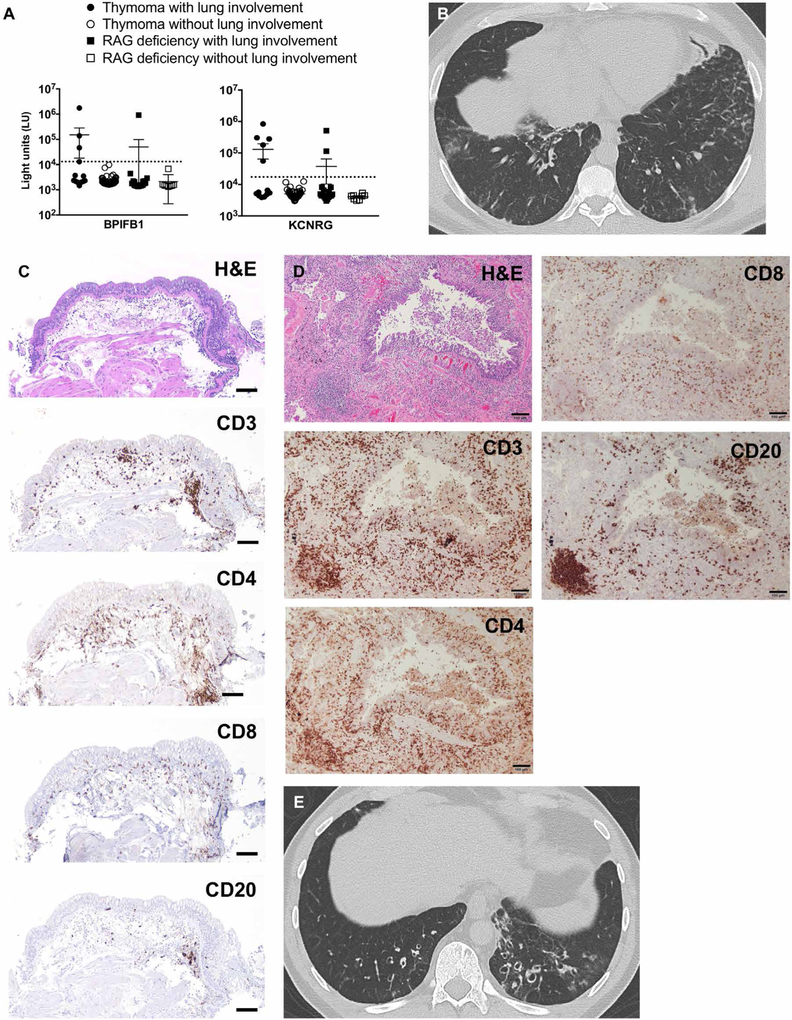
Fig. 6. Lung disease in patients with secondary AIRE deficiency exhibits shared features with APECED pneumonitis.
(A) Shown is the autoantibody immunoreactivity against BPIFB1 and KCNRG as light units (LU) using the luciferase immunoprecipitation systems (LIPS) immunoassay in 62 patients with thymoma with (n = 13) or without (n = 49) lung involvement, and in 27 recombination-activating gene (RAG)-deficient patients with (n = 19) or without (n = 8) lung involvement. Dotted lines represent the cutoff values for determining autoantibody seropositivity. (B) Representative chest CT image from a patient with thymoma with lung disease. (C and D) Representative images from an endobronchial (C) and transbronchial (D) biopsy of the same patient with thymoma with lung disease. Shown are H&E and immunohistochemical staining with the lymphocyte markers CD3, CD4, CD8, and CD20. Scale bars, 100 μm. (E) Representative chest CT image from a RAG-deficient patient with lung disease.