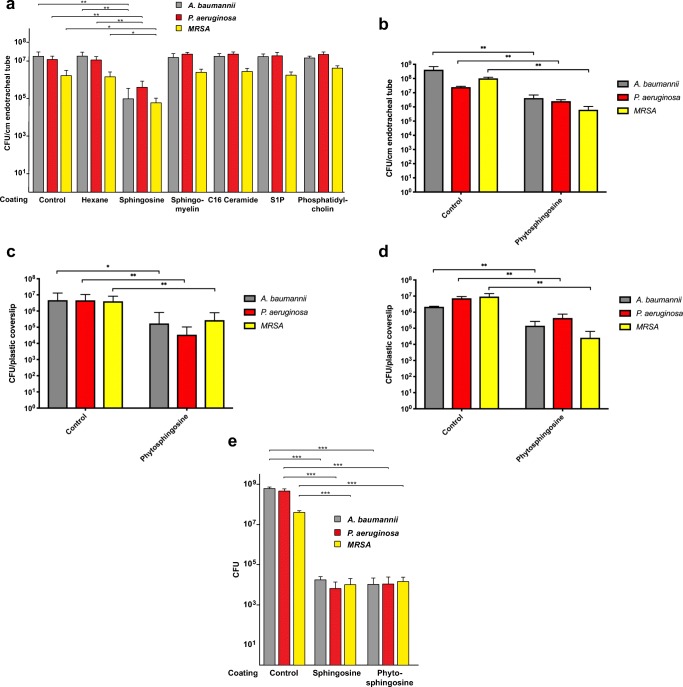
Fig. 1.
Antimicrobial efficacy of sphingosine and phytosphingosine-coated endotracheal tubes. a Uncoated vs vehicle (hexane)-coated vs sphingosine-coated and b vehicle (acetone)-coated vs phytosphingosine-coated 1-cm long segments of standard PVC endotracheal tubes were immersed for 12 h at 37 °C in bacterial suspension containing 1000 CFU of A. baumannii, P. aeruginosa, or methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA). Tube segments were then rinsed in H/S, sonicated to release adherent bacteria and bacterial counts (colony forming units, CFU) were determined. Hexane-coating did not significantly reduce bacterial adherence and growth on the plastic surface. Sphingosine-coated segments prevented 99.4% (p < 0.005), 97% (p < 0.005), and 97% (p = 0.05) bacterial adherence of A. baumannii (n = 6), P. aeruginosa (n = 6), and MRSA (n = 3), respectively. Coating with sphingomyelin, C16 ceramide, sphingosine 1-phoshate, or phosphatidylcholine was without effect on bacterial adherence/growth (n = 6 each). b Phytosphingosine-coated segments prevented 99.0% (p = 0.009), 90% (p < 0.005), and 99.4% (p < 0.005) bacterial adherence of A. baumannii (n = 5), P. aeruginosa (n = 5), and MRSA (n = 5), respectively. c Bacterial suspension containing 10,000 CFU in growth media was pipetted onto plastic coverslips, covered with plastic film, and incubated for 24 h at 37 °C. Coverslips were rinsed with H/S, incubated for 12 h, adherent bacteria were released from the surface via sonication, plated and counted after overnight growth. Phytosphingosine-coated coverslips prevented 96% (p = 0.02), 99% (p = 0.006), and 93% (p < 0.005) bacterial adherence of A. baumannii (n = 20), P. aeruginosa (n = 15), and MRSA (n = 20), respectively. d Bacterial suspension containing 10,000 CFU in growth media was pipetted onto plastic coverslips, covered with plastic film, and incubated for 24 h. Additional suspensions of 10,000 CFU were pipetted onto the coverslips after 24 h and 48 h. At 72 h, CFU on the cover slips were determined. Phytosphingosine-coated coverslips prevented 93% (p = 0.005), 94% (p = 0.005), and 99% (p = 0.03) bacterial adherence and growth of A. baumannii (n = 3), P. aeruginosa (n = 3), and MRSA (n = 3), respectively. e Small parts of the tubes were coated as indicated, 104 CFU of P. aeruginosa, A. baumannii or S. aureus were pipetted as a small drop onto the tube, incubated for 60 min, 500 μl TSB were added, and the bacteria were allowed to grow for 1 h. Aliquots of the cultures were then plated and CFU were determined after growth o/n (n = 6 each). Shown are mean ± SD, significant differences were compared to the respective control using ANOVA or t test, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001