Fig. 2.
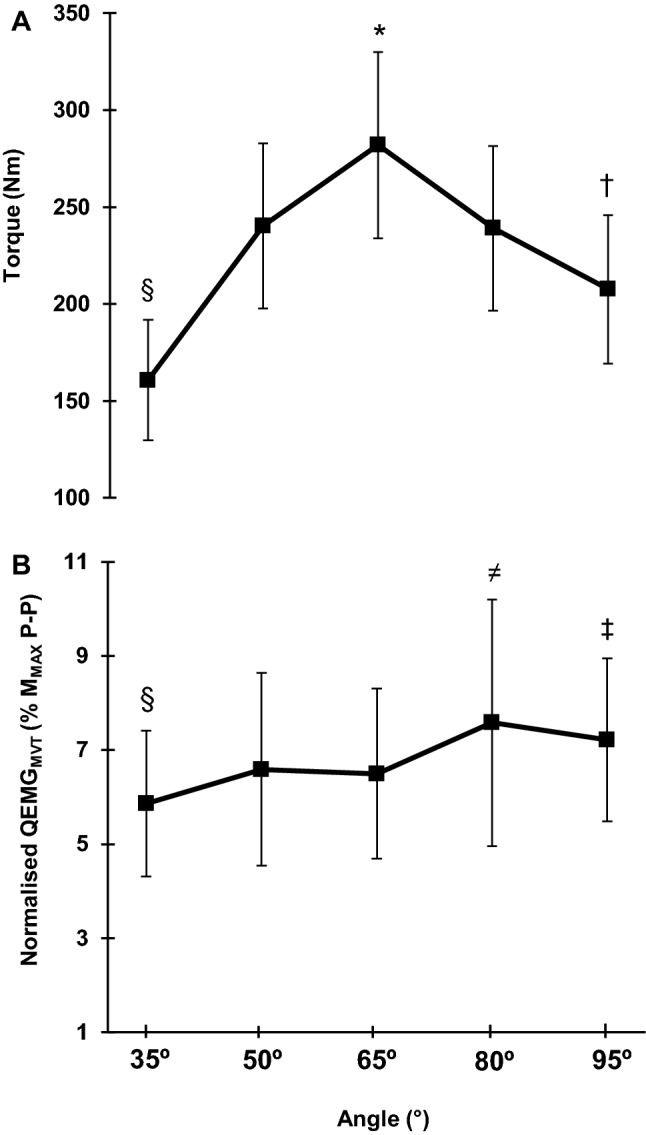
Knee extensor maximum voluntary torque (MVT)– and QEMGMVT–angle relationships during maximum isometric contractions performed at knee-joint angles of 35°, 50°, 65°, 80°, and 95°. Both relationships, MVT–angle (a) and QEMGMVT–angle (b), showed a main effect of angle (one-way ANOVA P < 0.001) with post-hoc differences denoted by: *higher than the other angles, §lower than the other angles, †lower than 50° and 80°, ≠higher than 35°, 50°, and 65°, and ‡higher than 65°. Data are mean ± SD (n = 28). MMAXP–P supramaximal M-wave peak-to-peak amplitude, QEMGMVT quadriceps femoris EMG at maximum voluntary torque
