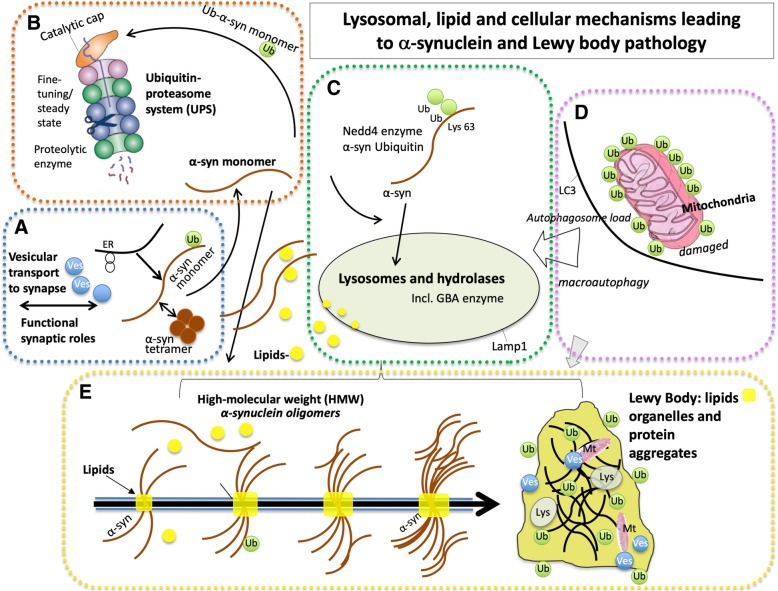
Fig. 2.
Lysosomal, lipid, and cellular mechanisms leading to α-synuclein and Lewy body pathology. a Under normal conditions α-synuclein is a natively structured protein with synaptic and vesicular functions. In addition to monomeric α-synuclein, α-synuclein can exist as physiological α-synuclein multimers (tetramers). α-Synuclein is normally transported to intracellular sites, including the synapse, where it participates in synaptic release functions. b Several pathways are involved in the degradation of α-synuclein and maintenance of its steady-state levels, including the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS), and c endo-lysosomal pathways. Overexpression of the ubiquitin ligase, Nedd4, can rescue α-synuclein toxicity in animal models through increased degradation of α-synuclein through the endo-lysosomal pathway (see text). c GBA haploinsufficiency, or deficiencies in other lysosomal enzymes, chaperones or transport proteins, can cause dysfunction of the lysosome in Parkinson’s disease (PD) and Lewy body dementia (LBD). Increased expression or function of lysosomal enzymes including GBA and Lamp1 reduce α-synucleinopathy and can rescue midbrain dopamine neuron degeneration in α-synucleinopathy preclinical models. d Damaged mitochondria are degraded through the mitophagy pathway, which can also be disrupted in aging and in familial PD and increases autophagic lysosomal load. e As described in this review, the structural similarity of α-synuclein with apolipoproteins suggests an additional role for α-synuclein in lipid transport. An aberrant accumulation of lipids, including glycosphingolipids in aging and in PD, are associated with abnormal lipidation of α-synuclein, and eventually accumulation of α-synuclein into insoluble high molecular weight forms. Mutations in, overexpression of, and loss of function of α-synuclein, contribute to cellular toxicities and pathology, including perturbation of lipid-vesicle trafficking and axonal transport. Recent advanced microscopic evidence shows that the Lewy body is composed of a large lipid core also including cellular organelles including mitochondria, lipids and protein aggregates. ER (endoplasmic reticulum), Lys (lysosome), Mt (mitochondria), Ub (ubiquitin), Ves (vesicle)