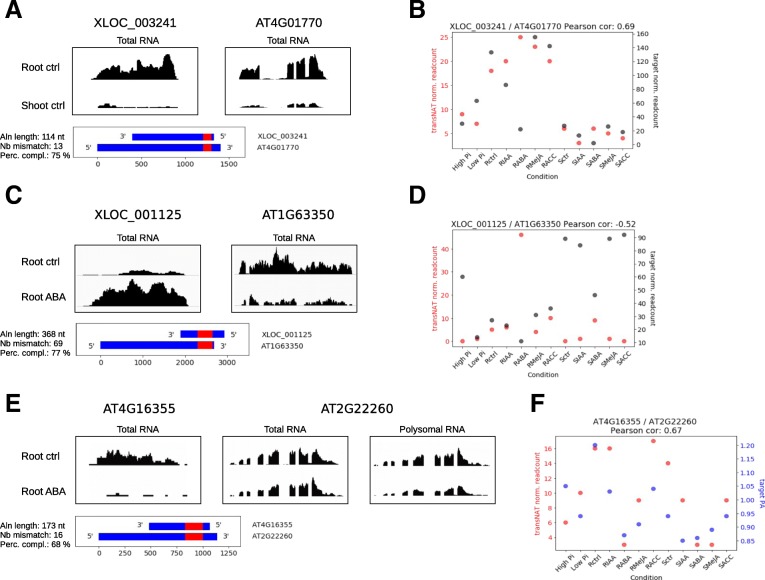
Fig. 2.
lincRNAs associated with changes of steady-state level or polysome association of potential target genes mRNA. a and b, Example of a pair showing a positive correlation between lincRNA and target gene mRNA expression. a, Density plots showing the density of RNAseq reads in untreated roots (Rctrl) or untreated shoots (Sctrl) for the lincRNA XLOC_003241 (left panel) and its potential target AT4G01770 (right panel). The region of complementarity between the transcripts (blue) is indicated in red on the diagram below. b, Correlation plot reporting the steady-state level of XLOC_003241 (red dots) and AT4G01770 (black) transcripts on the Y-axis for each of the 12 experimental conditions analyzed. The Pearson correlation coefficient is indicated on top. c and d, Example of a pair showing a negative correlation between lincRNA and target gene expression. Same legend as A-B for XLOC_001125 lincRNA and its potential target AT1G63350. e and f, Example of a pair showing a positive correlation between lincRNA steady-state level and target gene polysome association. e, Density plots showing the density of reads from total RNA-seq in untreated roots (Rctrl) or ABA treated roots (RABA) for the lincRNA AT4G16355 (left panel) and its potential target AT2G22260 (center panels). The right panel shows the density of reads from polysomal RNA-seq. The region of complementarity between the transcripts is indicated in red on the diagram below. f, Correlation plot reporting the steady-state level of AT4G16355 (red dots) and polysome association of AT2G22260 (blue) transcripts on the Y-axis for each of the 12 experimental conditions analyzed. The Pearson correlation coefficient is indicated on top. For A, C and E, details about the alignment length (Aln length), number of mismatch (Nb mismatch) and percentage of base complementarity (Perc compl) are indicated on the left of each panel showing the region of complementarity between the lincRNAs and the target mRNA