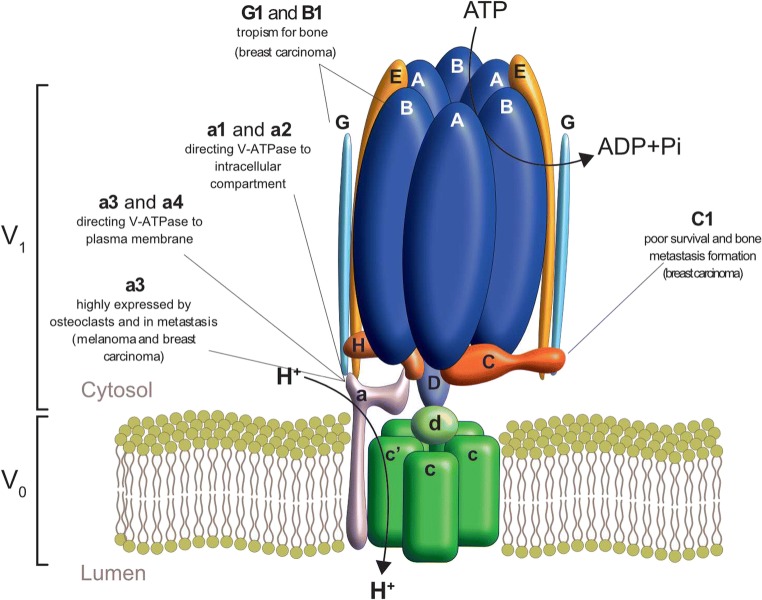
Fig. 1.
V-ATPase subunits in BM. The V-ATPase complex is formed by a peripheral domain (V1) responsible for ATP hydrolysis, and an integral domain (V0) that is involved in the translocation of protons across the cell membrane. The V1 domain is formed by a hexameric core of A-B subunits that participate to ATP binding and hydrolysis, and other seven ancillary proteins responsible for the rotation of the central core. The V0 domain includes a ring of proteolipid subunits inserted in the lipid bilayer. The role of V-ATPAse subunits that are relevant in BM is highlighted