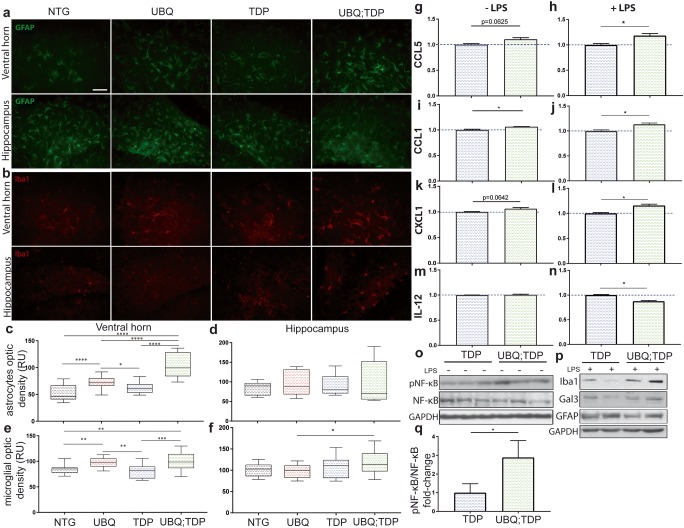
Fig. 6.
Gliosis and susceptibility to NF-κB-driven inflammation. a GFAP immunofluorescence of the ventral horn and hippocampus at 8 months of age (scale bar = 50 um, magnification = × 40). b Iba1 immunofluorescence of the ventral horn and hippocampus at 8 months of age. c GFAP signal measured with optic density in six different fields per mice in the ventral horn and d hippocampus (n = 3 mice per group). e Iba1 signal measured with optic density in six different fields per mice in the ventral horn and f hippocampus (n = 3 mice per group) (RU = random unit). Cytokines array levels of g–h CCL5, i–j CCL1, k–l CXCL1, m–n IL-12 in brain extracts of transgenic mice (TDP-43G348C and UBQLN2P497H; TDP-43G348C in blue and green, respectively) 24 h after intraperitoneal injection of LPS (n = 2) of without injection of LPS (n = 3). Only cytokines with significant changes are illustrated here. o Immunoblotting and SDS-PAGE analysis of the total brain extracts from non-injected mice (n = 3) and p the total brain extracts from LPS injected mice (n = 2). q Quantification of the pNF-κB levels vs NF-κB levels from brain extracts (n = 3)