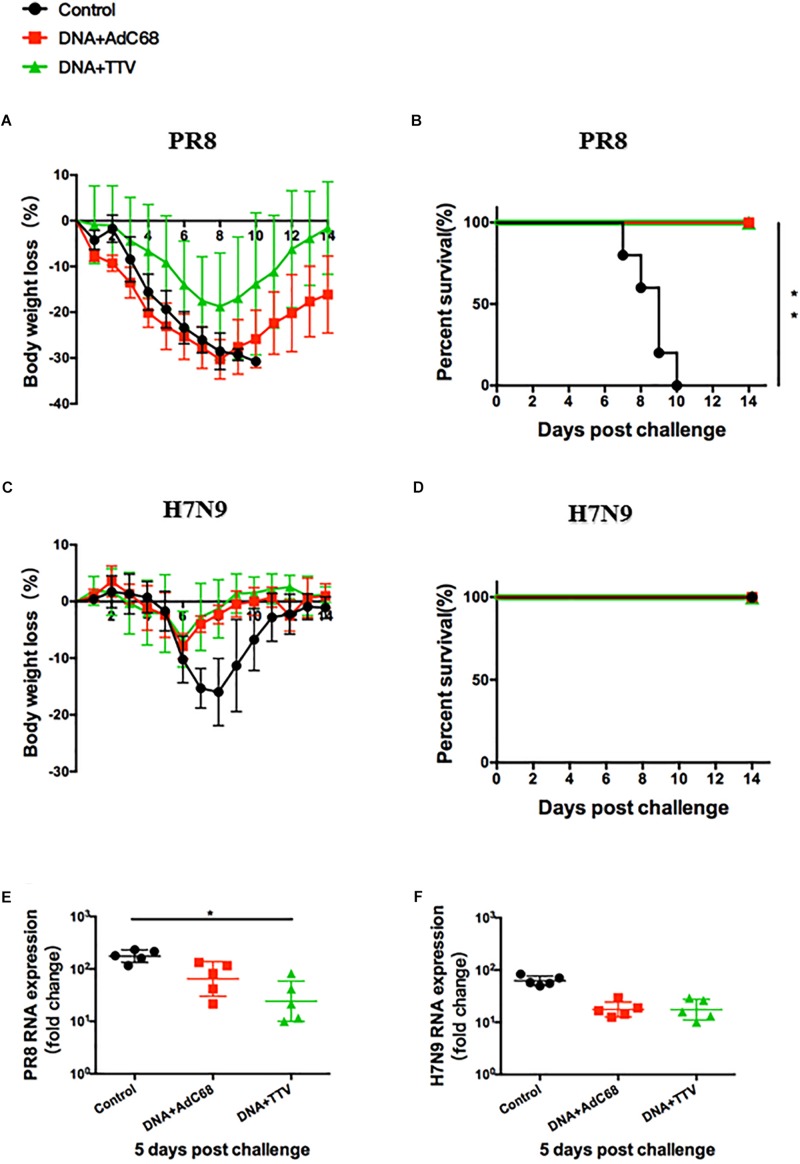
FIGURE 3.
DNA prime-viral vectored vaccine boost strategies conferred protection against PR8/(H1N1) and H7N9 viruses in vaccinated mice. Mice were immunized following schedule outlined in Figure 2A, and 4 weeks later challenged with either 500 50% tissue culture-infective dose (TCID50) of A/PR8(H1N1) or 100 TCID50 A/Shanghai/4664T/2013(H7N9) influenza virus. After infection, mice (n = 5 in each group) were monitored daily for body weight (A,C) or survival (B,D). Five mice in each group were sacrificed on day 5 post infection to isolate lung tissues for RNA extraction, followed by RT-PCR quantification of viral RNA to determine the relative viral loads (E,F). The error bars represent the SDs. Two-way ANOVA test, Mantel–Cox log rank test and t-test were used to determine difference in weight loss, lethality, and viral load, respectively. ∗∗p < 0.01; *p < 0.05.