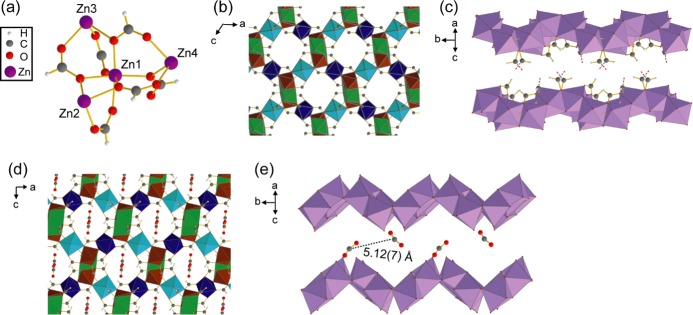
Figure 1.
(a) Connectivity between the four crystallographically inequivalent Zn centers in α-Zn3(HCOO)6. (b) Extended crystal structure of α-Zn3(HCOO)6, as viewed along the crystallographic b axis. Framework hydrogens are omitted for clarity. (c) Porous channel of α-Zn3(HCOO)6, as viewed perpendicular to the crystallographic b axis. The [ZnO6] units connecting the top and bottom of the channel are omitted for clarity. The C–O bonds between the omitted [ZnO6] units and the linker carbons are shown as red and gray dashed lines. (d) Extended crystal structure of CO2-loaded α-Zn3(HCOO)6, as viewed along the crystallographic b axis. (e) MOF channel as viewed perpendicular to the crystallographic b axis, showing the adsorbed CO2 locations and the distance between neighboring CO2. Distance error is given in parentheses. Hydrogens, framework carbons, and [ZnO6] units that connect the top and bottom of the channel are omitted. In all figures, carbon atoms are gray, oxygen atoms are red, hydrogen atoms are white, and zinc atoms are purple. Octahedra represent [ZnO6] units in (b)–(d), with different colors signifying [ZnO6] with crystallographically distinct Zn atoms in (b) and (d).