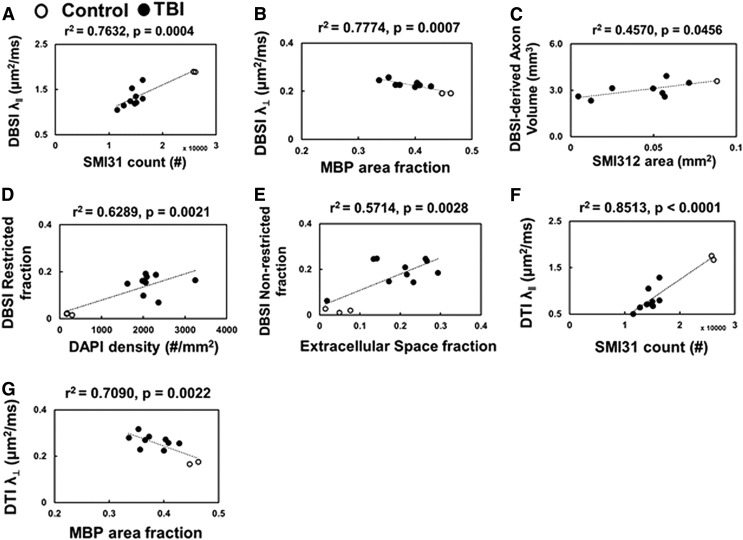
FIG. 5.
Diffusion basis spectrum imaging (DBSI) axial diffusivity (λ∥) and radial diffusivity (λ⊥), and DBSI-derived axon volume correlated with SMI-31 counts (A), myelin basic protein (MBP) area (B), and SMI-312 area (C), respectively, suggesting DBSI accurately reflects axon/myelin damage, inflammatory cell infiltration. DBSI-restricted isotropic diffusion fraction (putative cellularity) correlates with 4′,6-dianidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) density (D). DBSI non-restricted (putatively edema and tissue loss) also correlated with different degree of extracellular space (voids) in hematoxylin and eosin (E), reflect the extent of lost tissues. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) (λ∥ and λ⊥ were consistent with SMI-31 counts (F), MBP area (G), but appear somewhat exaggerated compared with DBSI λ∥ and λ⊥ due to increased cellularity and vasogenic edema associated with inflammation (see Fig. 2).