Figure 3. An approach to design allosteric protein switches.
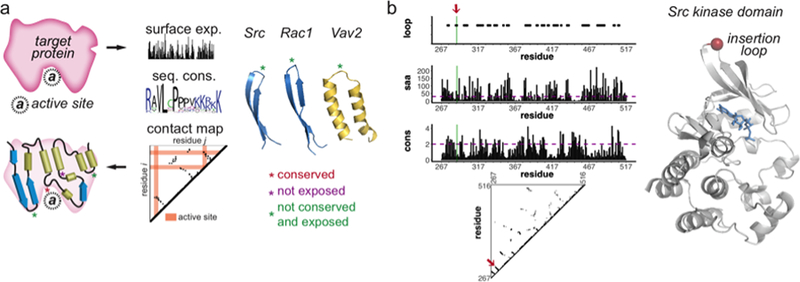
a) The three dimensional structure or a structural homolog can be used to identify secondary structures, surface exposure of each residue, and the contact map. By collecting sequences from different species and homologue domain sequences, sequence conservation is calculated and used to identify surface sequences less likely to be important for function. The insertion sites (shown with green asterisks) are tight surface loops connecting interacting elements of interior secondary structure (e.g. two parallel strands or helices) b) Src kinase domain was used as an example. The loop sites along with other parameters, including solvent accessible area (saa) and sequence conservation (cons), contact map were used to identify insertion sites. The red arrow on the plots and red sphere on the structure indicates the site that was selected.
