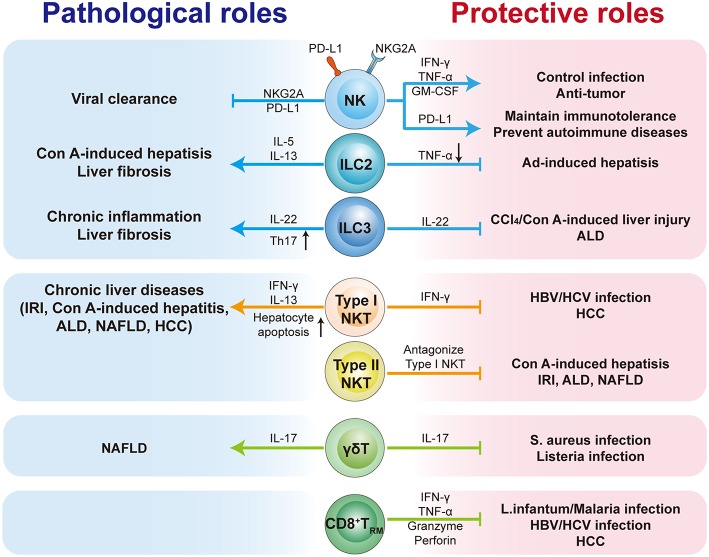
Figure 1.
The pathological or protective roles of liver-resident lymphocytes in liver diseases. The liver contains multiple types of tissue-resident lymphocytes, including CD8+TRM cells, NK cells, ILCs, γδT cells, and NKT cells. Liver-resident lymphocytes serve as the first line of defense in response to infection and non-infectious insults, and play roles in immunosurveillance, immune regulation, and the maintenance of liver homeostasis. Liver-resident lymphocytes generally exert protective or pathological effects via producing antimicrobial or homeostatic effector molecules, and by cooperating with other immune cells. They are involved in many kinds of liver diseases, such as metabolic liver diseases (e.g., ALD and NFALD), acute liver injury, liver fibrosis, viral hepatitis, and hepatic carcinoma (HCC). Modulation of liver-resident lymphocytes responses may represent promising therapeutic method to treat liver diseases.