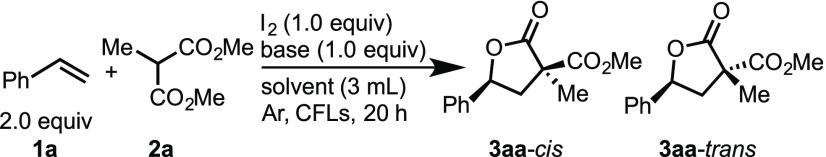
Table 1. Optimization of the Intermolecular Lactonization of Styrene 1a with Malonate (2a)a.
| entry | base | solvent | 3 (%) | dr (cis:trans)b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ca(OH)2 | tBuOH | 83 | 79:21 |
| 2 | Mg(OH)2 | tBuOH | trace | |
| 3 | Ba(OH)2 | tBuOH | 74 | 67:33 |
| 4 | Sr(OH)2 | tBuOH | 33 | 50:50 |
| 5 | BaCO3 | tBuOH | trace | |
| 6 | SrCO3 | tBuOH | trace | |
| 7 | NaHCO3 | tBuOH | 32 | 50:50 |
| 8 | Na2CO3 | tBuOH | 77 | 45:55 |
| 9 | K2CO3 | tBuOH | 53 | 40:60 |
| 10 | Cs2CO3 | tBuOH | 49 | 37:63 |
| 11 | KOH | tBuOH | 36 | 33:67 |
| 12 | K3PO4 | tBuOH | 26 | 30:70 |
| 13 | Na2CO3 | tBuOH/H2O (2 mL/1 mL) | 69 | 25:75 |
| 14 | Ca(OH)2 | tBuOH/H2O (2 mL/1 mL) | 61 | 40:60 |
| 15 | Ba(OH)2 | tBuOH/H2O (2 mL/1 mL) | 7 | 29:71 |
| 16 | Sr(OH)2 | tBuOH/H2O (2 mL/1 mL) | 29 | 42:58 |
| 17 | K2CO3 | tBuOH/H2O (2 mL/1 mL) | 60 | 26:74 |
| 18 | Cs2CO3 | tBuOH/H2O (2 mL/1 mL) | 56 | 28:72 |
| 19 | KOH | tBuOH/H2O (2 mL/1 mL) | trace | |
| 20 | K3PO4 | tBuOH/H2O (2 mL/1 mL) | 41 | 27:73 |
Reaction conditions: 1a (2 equiv), 2a (0.3 mmol), I2 (0.3 mmol), and base (0.3 mmol) in solvent (3 mL) were stirred at ambient temperature irradiated with four of compact fluorescent lamps (CFLs) for 20 h.
Diasteromeric ratios (dr) were determined by 1H NMR analysis of the crude reaction mixture.