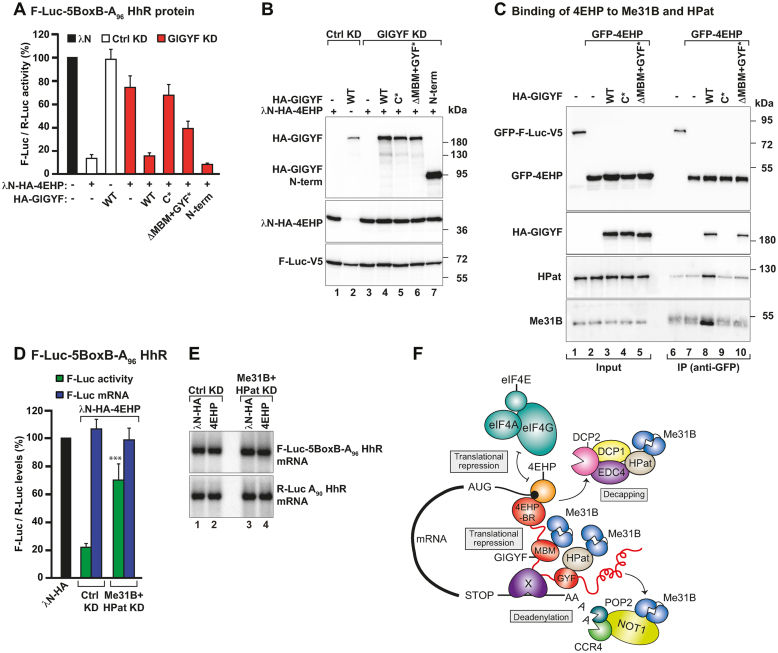
Figure 5.
GIGYF recruits Me31B and HPat to 4EHP-repressor complexes. (A) A complementation assay using the F-Luc-5BoxB-A96-HhR reporter and λN-HA-4EHP was performed in Ctrl and GIGYF-depleted cells expressing HA-GIGYF proteins (dsRNA-resistant and either WT, mutants or the N-term). A plasmid expressing R-Luc-A90-HhR served as a transfection control. Samples were analyzed as described in Figure 1A. (B) Western blot analysis showing the expression of the λN-HA-4EHP, HA-GIGYF and F-Luc-V5 proteins used in the complementation assay. (C) Interaction of GFP-4EHP with endogenous Me31B and HPat proteins assayed by anti-GFP immunoprecipitation in the presence or absence of HA-GIGYF (WT or mutants). GFP-F-Luc-V5 was used as a negative control. The inputs (4% for GFP- and HA-tagged proteins and 0.1% for Me31B and HPat) and bound fractions (5% for GFP- and HA-tagged proteins and 20% for Me31B and HPat) were analyzed by western blotting using anti-GFP, anti-HA, anti-Me31B and anti-HPat antibodies. (D, E) S2 cells were treated with dsRNA targeting neomycin (Ctrl KD) or Me31B and HPat mRNAs (Me31B+HPat KD) and transfected with a mixture of three plasmids coding for F-Luc-5BoxB-A96-HhR, R-Luc-A90-HhR and the indicated λN-HA-tagged proteins. In panel D, F-Luc activity and mRNA levels were normalized to that of R-Luc in the presence of the different tethered proteins. Samples were analyzed as described in Figure 1A. Panel E shows a representative northern blot. The P value (***P < 0.0005) was determined using the two-tailed Student's t test. (F) Model for the assembly of a 4EHP-repressor complex. 4EHP (orange) is the cap-binding protein that blocks eIF4F mRNA recruitment. GIGYF (red) provides binding sites for 4EHP (4EHP-BR), Me31B (MBM), HPat (GYF domain) and the CCR4–NOT deadenylase complex. Additionally, GIGYF might also bind an unknown RNA-binding protein (X) or directly interact with the target mRNA. HPat and the CCR4–NOT complex also can interact with Me31B (24,40,41). The formation of this complex ensures that multiple mechanisms are employed to robustly suppress target mRNA expression: translational repression, deadenylation and decapping, which is subsequently followed by degradation of the mRNA.