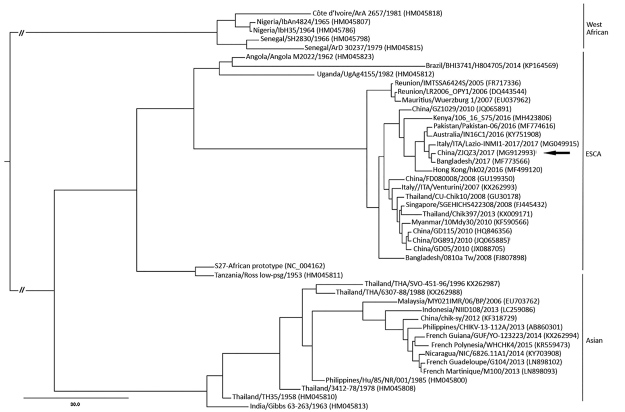
Figure.
Phylogenetic analysis of the complete CHIKV genome sequences of isolate ZJQZ3 from Quzhou, Zhejiang Province, China (arrow), and reference sequences. Dataset-specific models that were selected using the Akaike Information Criterion in Modeltest 3.7 (http://darwin.uvigo.es/our-software) were analyzed. Maximum-likelihood (ML) analysis was processed in RAxML v7.2.8 (http://sco.h-its.org/exelixis/software.html). The optimal ML tree and bootstrap percentages (BP) were estimated in the same run. The ML BP values were obtained from 1,000 bootstrap replicates using the rapid bootstrap algorithm. BEAST 1.6 (http://beast.community/programs) was employed to construct a Bayesian maximum clade credibility tree based on an uncorrelated exponential distributed relaxed-clock model for our sample. The genotypes of CHIKV were divided into West African, ECSA, and Asian. Virus lineages are shown at right. GenBank accession numbers are given in parentheses. Scale bar indicates nucleotide substitutions per site. CHIKV, chikungunya virus; ECSA, East/Central/South African.