Figure 3.
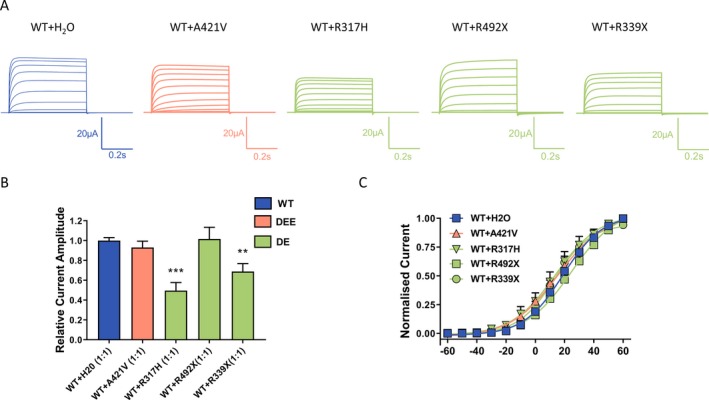
Dominant‐negative effect of Kv3.1 variants. (A) Representative current traces recorded from Xenopus laevis oocytes injected with the same amount of cRNA encoding Kv3.1a wild‐type with addition of either H2O or the same amount cRNA encoding Kv3.1 variants in a 1:1 ratio. (B) Current amplitudes analyzed at the end of the voltage step to + 60 mV and normalized to the mean current amplitude of WT + H2O recorded on the same day revealed a significant reduction for R317H and R339X but not for the A421V coexpression, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01 using one‐way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test; WT + H2O (n = 111), WT + A421V (n = 62); WT + R317H (n = 11); WT + Q492X (n = 21); WT + R339X (n = 17). (C) Conductance‐voltage relationships of the WT and its coexpressions with A421V, R317H and R339X. V0.5 and slope factor (k) values were as follows: for WT + H2O 18.2 ± 1.4 mV, 12.4 ± 0.4 (n = 27), for WT + A421V 16.6 ± 1.8, 15.2 ± 0.4 (n = 36), for WT + R317H 21.1 ± 4.5 mV, 17.8 ± 1.9 (n = 8), for WT + Q492X 25 ± 3 mV, 13.9 ± 0.5 (n = 12), and for WT + R339X 15.8 ± 3.1 mV, 12.2 ± 1.1 (n = 15).
