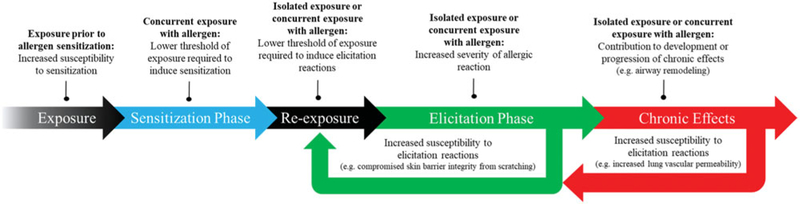
Figure 3.
Potential adverse outcomes with respect to the sensitization and elicitation phases of allergy following exposure to immunotoxic agents. Adjuvant effects resulting from exposure prior to allergen sensitization can manifest as increased susceptibility to sensitization. Exposure concurrent to sensitization may lower the threshold of allergen exposure required to induce sensitization. Following sensitization to allergen, exposure to an immunotoxic agent either in the absence or presence of allergen may result in a lower threshold of exposure required to induce elicitation reactions or increased severity of elicitation symptoms. These effects may further increase susceptibility to elicitation reactions as result of physiological alterations such as compromised skin barrier integrity. Furthermore, isolated exposure to immunotoxic agents or concurrent to allergens in established allergic disease conditions may also contribute to the progression of chronic effects, such as airway remodeling, which can also further contribute to elicitation reactions.