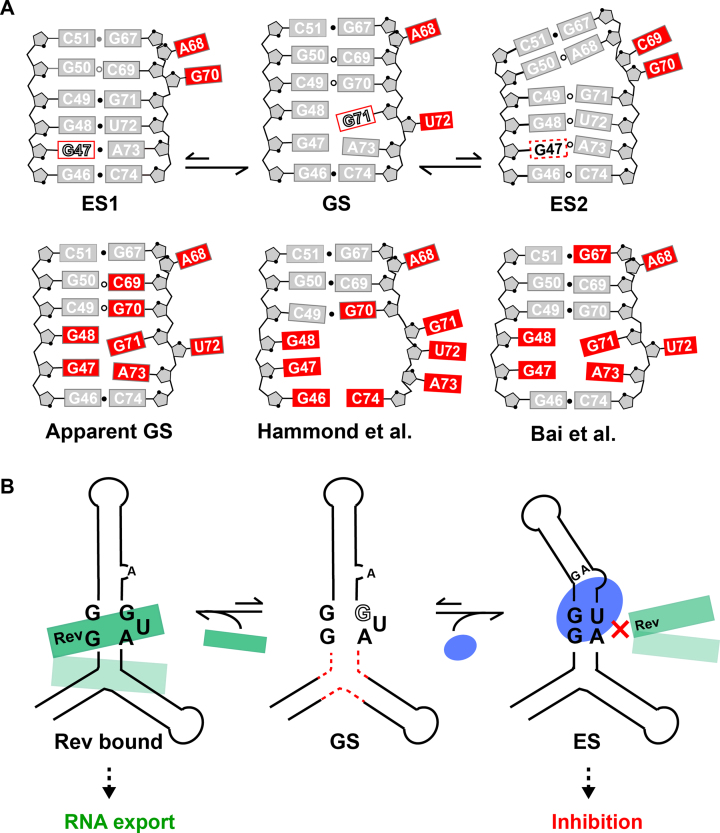
Figure 6.
Implications of RRE dynamic ensemble. (A) The RRE ES ensemble results in different conformations that expose different nucleotides for reactivity. This could contribute to high reactivity (apparent GS) at several nucleotides (colored in red), including ones that may form canonical pairs in the GS. Results are compared with SHAPE reactivity measured previously by Hammond et al. (90) and Bai et al. (42). The syn base in GS and ES1 are indicated using red rectangles and open letters. Residues in syn to anti conformational exchange are indicated using dashed rectangles. (B) Proposed role for RRE ESs in providing mechanisms for conformational cooperativity during Rev (in green) recognition by organizing the secondary binding site (dashed red lines). Stabilization of ESs using small molecules (in blue) could provide a strategy for inhibiting Rev binding and viral RNA export for anti-HIV therapeutics. The syn base is indicated using open letters.