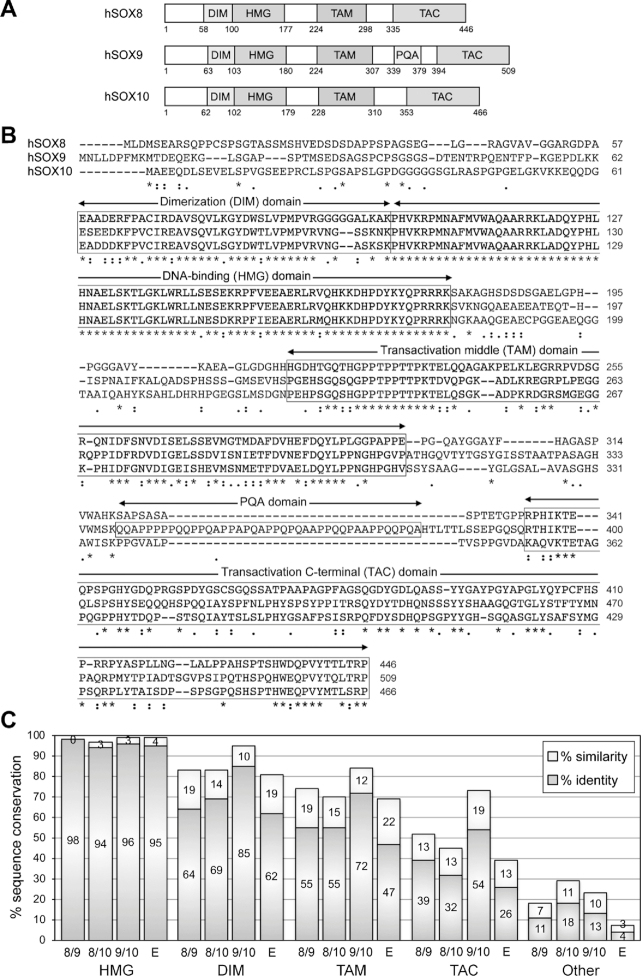
Figure 1.
Sequence conservation among the human SOXE proteins. (A) Schematic showing the domain organization of the three human SOXE proteins. Conserved domains are shown with boxes and the amino acids at the boundaries of the protein and domains are indicated with numbers. DIM, homodimerization domain; HMG, DNA-binding domain; TAM, transactivation domain located in the middle of the proteins; PQA, P-, Q- and A-rich domain in SOX9; TAC, carboxy-terminal transactivation domain. (B) ClustalW alignment of the amino acids of the human SOXE proteins. The dimerization (DIM), DNA-binding (HMG), middle transactivation (TAM) and C-terminal transactivation (TAC) domains are boxed. Stars indicate identical residues and dots indicate similar residues. Numbers indicate residue positions within the proteins. (C) Graph showing the degrees of protein conservation. The percentages of sequence identity and similarity were calculated by ClustalW alignment. They are shown for each conserved domain and for the rest of the protein sequences (other). SOX8 is compared to SOX9 (8/9), SOX8 to SOX10 (8/10), SOX9 to SOX10 (9/10) and the three proteins together (E).