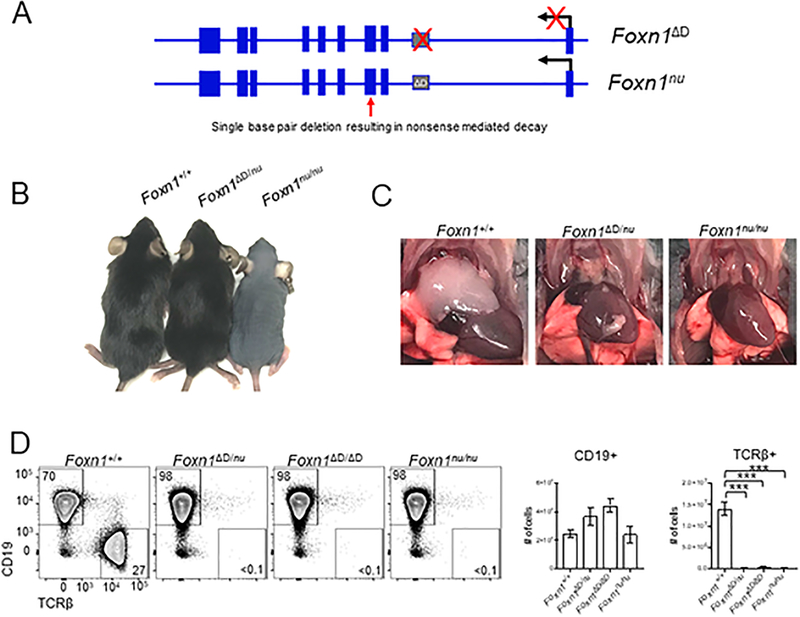
Figure 6.
The Foxn1D RE is specific to Foxn1 and functions in cis. (A) Comparison of the mutations of the Foxn1 gene in Foxn1ΔD/ΔD and Foxn1nu/nu mice. (B) Images of Foxn1+/+, Foxn1ΔD/nu, and Foxn1nu/nu mice showing normal overall fur coat in the Foxn1ΔD/nu mouse. (C) The Foxn1ΔD/nu mouse lacks a normal appearing thymus just like the Foxn1nu/nu mouse. (D) Flow cytometric analysis was used to examine TCRβ+ cells in the spleen. Total cell numbers were calculated from DAPI- cells. There is a significant loss of TCRβ+ cells in the Foxn1ΔD/nu mouse however there is no difference in the overall number of TCRβ+ cells in the Foxn1ΔD/nu mouse compared to the Foxn1ΔD/ΔD and Foxn1nu/nu mice. Total cell numbers were calculated from DAPI- live cells and shown as mean ± SEM for n = 3–4 mice (4–8 weeks old) per genotype. ANOVA was performed to determine statistical significance. *** p < 0.001.