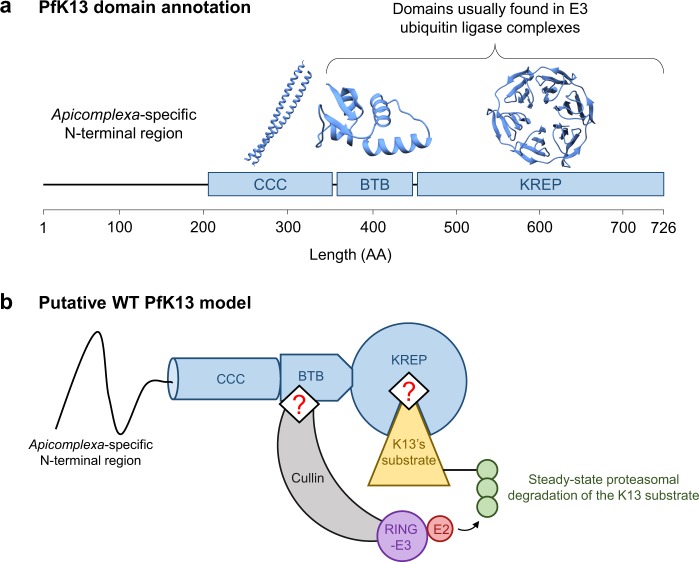
Figure 1.
Schematic and structural representation of PfK13 and its putative function as substrate adaptor. (a) PfK13 domain annotation. Three domains of PfK13 are annotated in databases: coiled-coil-containing (CCC), BTB, and Kelch-repeat propeller (KREP). The Apicomplexa-specific N-terminal domain is predicted to exhibit a random-coil conformation. The crystal structure of BTB and KREP domains was solved; the CCC domain is expected to form two helices coiling together. (b) Proposed, simplified model of the protein complex containing PfK13, based on PfK13 domain annotation and co-immunoprecipitation experiments17,21,22,89,90. The BTB domain of PfK13 is expected to bind a scaffold Cullin protein, while the KREP domain likely binds to the substrate molecule(s) further ubiquitinated and possibly degraded by the proteasome. Importantly, the regions and sites of PfK13 involved in binding are unknown (represented as red ‘?’ symbol in the figure). For ease of representation, PfK13 was shown as a monomer although the crystal structure of PfK13 BTB-KREP was solved as a dimer.