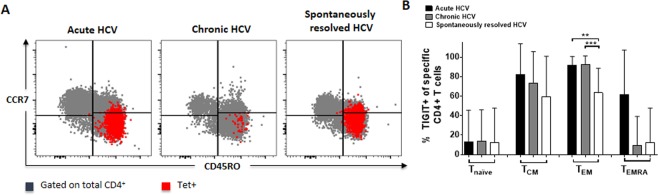
Figure 2.
(A,B) Memory subset distribution of TIGIT+, HCV-specific CD4+ T cells of HCV patients with acute, chronic and spontaneously resolved infection. The differentiation markers CD45RO and CCR7 were used to analyse the ex vivo expression of TIGIT+ HCV-specific MHC class II tetramer+ CD4+ T cells within different memory T cell subsets. (A) Representative large dot plots depicting the memory subset distribution of TIGIT+ HCV-specific MHC class II tetramer+ CD4+ T cells (red) on an overlay of gated total CD4+ cells (grey) of patients with acute, chronic and spontaneously resolved HCV infection; memory subset definition: CCR7−/CD45RO–terminal effector T cells-TEMRA; CCR7+/CD45RO–naïve T cells-Tnaïve; CCR7−/CD45RO+–effector memory–TEM; CCR7+/CD45RO+–central memory–TCM. (B) Comparison of the TIGIT receptor expression of HCV-specific MHC class II tetramer+ CD4+ T cells and different memory T cell subsets in patients with acute (n = 10), chronic (n = 11), and spontaneously resolved (n = 8) infection. P values were calculated by the Tukey’s multiple comparison test. P-values smaller than 0.05 were considered significant, where *,** and *** indicate p-values between 0.01 to 0.05, 0.001 to 0.01 and 0.0001 to 0.001 respectively.