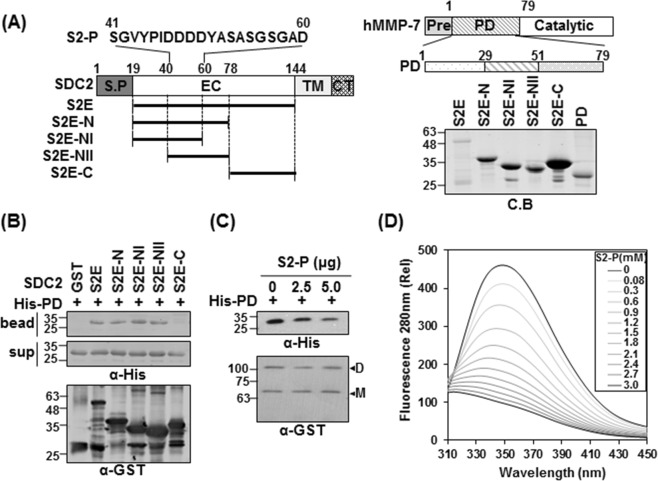
Figure 1.
The N-terminus of syndecan-2 interacts with the pro-domain of MMP-7. (A) Schematic representation of the syndecan-2 core protein (SDC2) and MMP-7. The signal peptide (SP), the extracellular domain (EC), the transmembrane domain (TM), and the cytoplasmic domain (CT) of syndecan-2 are noted, and the various deletion mutants are indicated. A peptide corresponding to residues 41–60 of the syndecan-2 extracellular domain (S2-P) was synthesized. Syndecan-2 is labeled with amino acid numbers to show the location of each deletion (left). Schematic representation of MMP-7. The pre-domain (Pre), pro-domain (PD), and catalytic domain are shown (right top). Purified GST-SDC2 mutants and the His-tagged pro-domain of MMP-7 were separated by 15% SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie Blue (right bottom). (B) Purified GST or GST-SDC2 mutants were incubated with His-tagged pro-domain of MMP-7 (His-PD). Bound materials were subjected to immunoblotting with an anti-His tag antibody (top). The membranes were then stripped and re-probed with an anti-GST antibody (bottom). (C) Purified GST-SDC2 was incubated with purified His-PD MMP-7 plus the indicated amounts of S2-P for 2 h at 4 °C. Bound materials were subjected to immunoblotting with an anti-His tag antibody (top). The membranes were then stripped and re-probed with an anti-GST antibody (bottom). M and D indicate monomer and dimer of syndecan-2, respectively. (D) Fluorescence spectroscopy indicates the binding affinity between His-PD and S2-P peptide. Titration between His-PD and S2-P peptide was performed up to 1 by 200 molar ratios and the Kd value was calculated as 1.586 ± 0.012 mM.