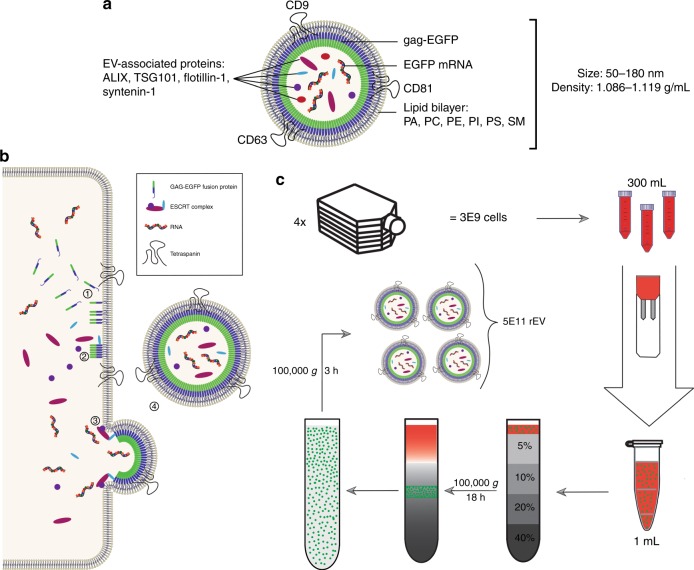
Fig. 1.
rEV are separated from conditioned medium using density gradient centrifugation. a Schematic representation of rEV showing representative molecular components shared with sample EV, PA phosphatidic acid, PC phosphatidylcholine, PE phosphatidylethanolamine, PI phosphatidylinositol, PS phosphatidylserine, SM sphingomyelin. b Schematic overview of the production of rEV at the cellular level: (1) The gag-EGFP fusion protein inserts in regions of the plasma membrane enriched for tetraspanins CD9, CD63 and CD81 via its N-terminal MA domain containing a myristoyl group. (2) The gag-EGFP fusion protein oligomerizes and recruits ESCRT-1 proteins (TSG101) via the PTAP motive on its p6 domain. (3) Recruitment of ESCRT-2/3 proteins initiates the outward budding of the gag-EGFP containing plasma membrane. (4) ESCRT-3 mediated scission of the membranes finally causes release of rEV into the conditioned medium (CM)13. c Schematic overview of the workflow to separate rEV from CM of gag-EGFP transfected HEK293T cells. Seventy-two hour post transfection CM is collected from ~3 x 109 cells and concentrated to 1 mL. Concentrated CM is loaded on top of an OptiPrep density gradient (ODG) and centrifuged for 18 h at 100,000 × g. Density fractions of 1.086–1.119 g/mL are collected and pelleted for 3 h at 100,000 × g resulting in ~5 x 1011 rEV per harvest