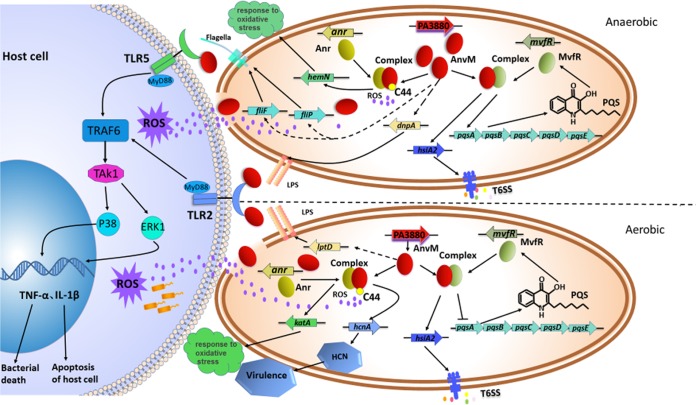
FIG 6.
Model of AnvM-mediated regulation and its interaction with host cell. The regulatory pathways of AnvM are proposed based on our current observations and previous studies. In the present study, we demonstrated that AnvM interacted with MvfR and Anr. Under anaerobic conditions, AnvM is expressed at a high level and interacts with MvfR to promote the expression of hsiA and pqsA, thus activating the T6SS and QS system. hemN was positively regulated by AnvM after interacting with Anr, which senses oxygen levels and responds to oxidative stress. AnvM positively regulates fliF, flip, and dnpA to synthesize flagella as well as LPS, which leads to activation of TLR5 and TLR2 to turn on the pathways of p38 and ERK1. Under aerobic conditions, AnvM interacts with MvfR, which induces expression of hsiA to regulate the T6SS and represses expression of pqsA to regulate the QS system. katA and hcnA are positively regulated by the AnvM-Anr complex. AnvM positively regulates lptD to regulate LPS, which activates the p38 or ERK1 pathway of TLR2. In addition, Cys44 is a critical site for AnvM function, which senses ROS produced by the host immune system. AnvM also directly interacts with TLR2 and TLR5 to activate the pathways of p38 or ERK1, which causes host immune response. Solid arrows indicate positive regulation, and solid T-bars present negative regulation. Solid lines or dotted lines represent direct or indirect regulatory relationships that were established, respectively.