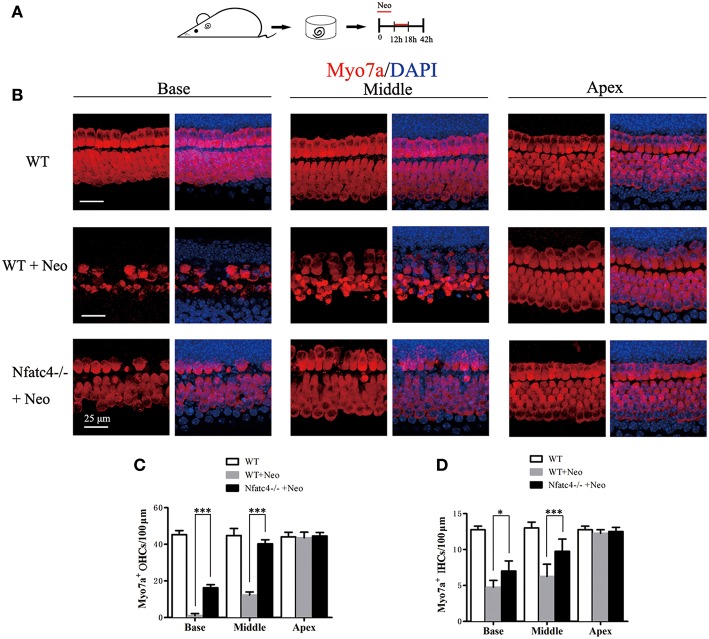
Figure 2.
Cochlear hair cells in Nfatc4−/− mice showed reduced sensitivity to aminoglycoside antibiotic-induced ototoxicity. (A) The diagram of the assay. Cochlear sensory epithelium samples from P2 Nfatc4−/− and WT mice were dissected out and allowed to recover for 12 h. The samples were treated with 1 mM neomycin for 6 h, allowed to recover for 24 h, and then used for immunostaining. (B) The representative Myo7a immunofluorescence staining of sensory epithelium from Nfatc4−/− and WT mice after neomycin treatment. (C,D) Quantification of inner hair cells (IHCs) and outer hair cells (OHCs). The numbers of IHCs and OHCs in the middle and basal turns were significantly greater in the cochlear epithelium from Nfatc4−/− mice than in WT mice after neomycin treatment. Scale bar = 25 μm. *indicates p < 0.05 and ***indicates p < 0.001. n = 5.