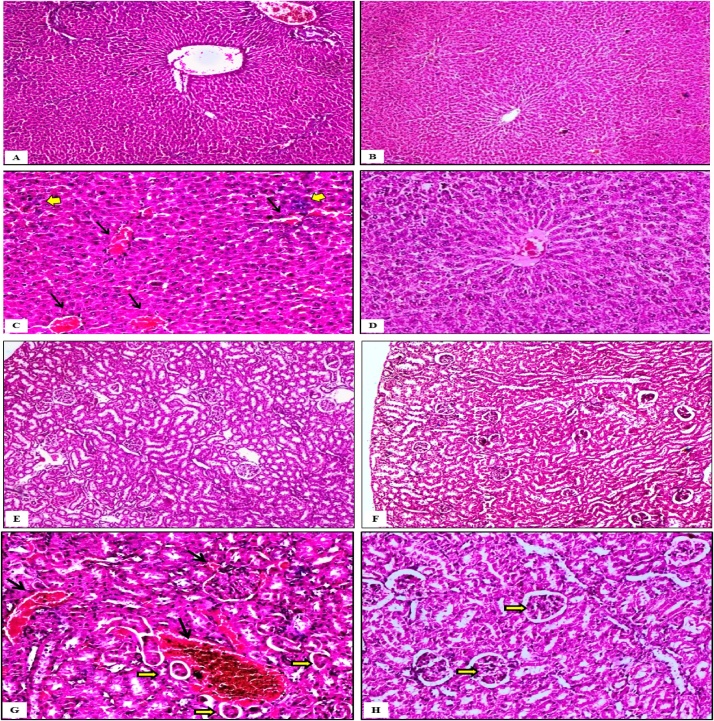
Plate 1.
Photomicrograph for experimental design done on female Sprague-Dawley rats classified into 4 groups and the route of administration is intraperitoneal injection: Group (1) control, Group (2) Rats treated with P. oleracea ethanolic extract (2 mg/kg bw), Group (3) rats treated with CdCl2 (3.5 mg/kg bw), Group (4) rats treated with (CdCl2 3.5 mg/kg bw + P. oleracea 2 mg/kg bw). All tissues pecimens were stained with H&E stain.
Liver: Fig A: Control group (1) showed completely normal tissue details in liver X 100. Fig B: group (2) liver exhibited normal tissue characters without histopathological changes X 100. Fig C: Liver of group (3) showed severe congestion in the central veins of hepatic lobules accompanied with hemorrhages among the hepatic cords (black arrows). Mild multifocal infiltrations of inflammatory cells among several hemorrhagic areas (yellow arrows) were noticed X 200. Fig D: Liver of the fourth group exhibited recovery of the hemorrhagic and inflammatory condition and the hepatic tissue return to normal X 200.
Kidney: Fig E: control group showed the normal renal tissue X 100. Fig F: group (2) kidney exhibited no histopathological changes than normal X 100. Fig G: Kidney of group (3) clarified severe congestion in most of the renal blood vessels associated with multifocal extravasation of blood among the proximal convoluted tubules and in the peri glomerular areas (black arrows). Also, severe atrophy in large numbers of the renal tubules in the peri vascular areas (yellow arrows) was observed X 200. Fig H: Kidney of group (4) the renal tissue became completely normal except presence of mild degeneration in the lining epithelium of proximal convoluted tubules (yellow arrows) X 200.