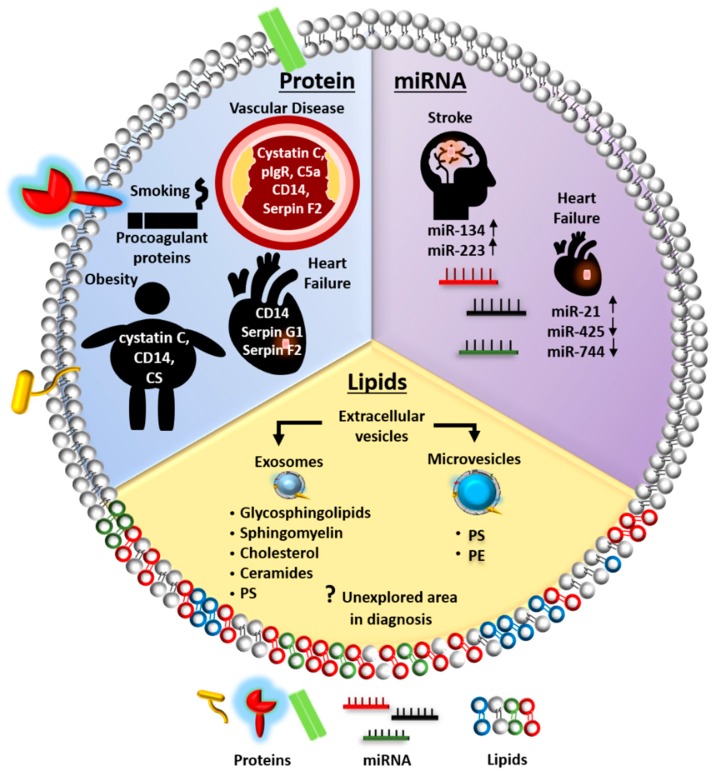
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram illustrating EVs as an alternative source of biomarkers in cardiovascular disease (CVD). Extracellular vesicle (EV) proteins, such as CD14, cystatin C and coagulation-related proteins including Serpin G1 and Serpin F2, have been proposed as novel biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of heart failure, vascular disease, and stroke. Conventional CVD risk factors, such as obesity and smoking, have been associated with EV protein contents, including CD14, cystatin C, and procoagulant proteins. Certain EV miRNAs have also been identified as novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for stroke and heart failure. Five EV miRNAs are listed as representatives. EV lipids, however, remain largely unexplored in the diagnosis or prognosis of CVD. CVD, cardiovascular diseases; CS, complement system; C5a, complement factor 5a; pIgR, polygenic immunoglobulin receptor; PS, phosphatidylserine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine.