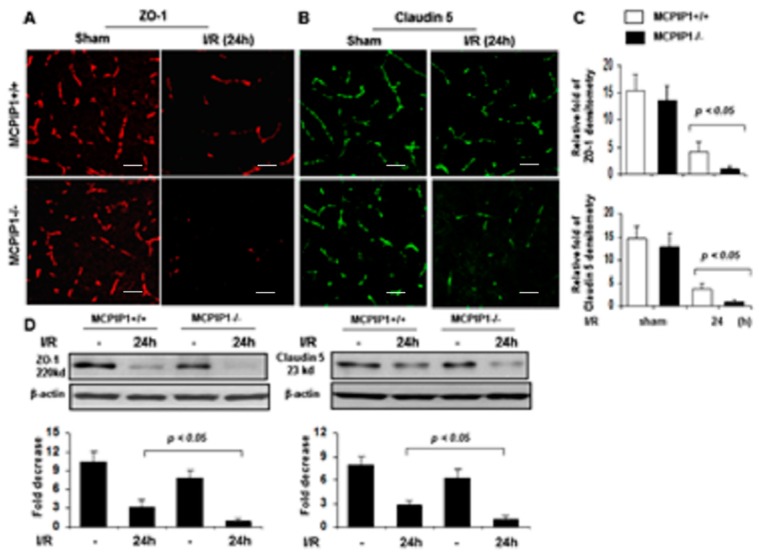
Figure 4.
Altered expression of tight junction proteins zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) and claudin-5 in the brains of MCPIP–/– mice subjected to transient focal ischemia/reperfusion. (A,B) Representative photomicrographs of immunofluorescence staining using AlexaFluor®-conjugated secondary antibodies. The red fluorescence indicates expression of ZO-1 and the green fluorescence indicates expression of claudin-5 in brain sections of the MCPIP1–/– mice and their wild-type littermates subjected to 2 h of MCAO followed by 24 h of reperfusion. The relative levels of ZO-1 and claudin-5, assessed by immunofluorescence intensity, are presented in bar graphs (C). Levels of ZO-1 and claudin-5 were significantly reduced in the MCPIP1–/– mice compared to that seen in their wild-type littermates subjected to 24 h of reperfusion after 2 h of MCAO. Values represent mean ± SD. p < 0.05, n = 6 per group. (D) Protein extracts from the mice brains were subjected to immunoblot analysis with anti-ZO-1 or anti-claudin 5 antibodies, and β-actin served as a loading control (Upper panels). Bar graphs show the levels of ZO-1 (Lower panel, left) and claudin-5 (Lower panel, right), assessed by densitometric analysis normalized by β-actin protein levels and expressed as fold change compared the sham-operated animals. Levels of ZO-1 and claudin-5 in the brain of the MCPIP1–/– mice were significantly reduced compared to that seen in their wild-type littermates subjected to 24 h of reperfusion after MCAO I/R hemisphere was measured by western blot with mixed samples of three independent experiments. Values represent mean ± SD. p < 0.05 between the MCPIP1–/– mice and their wild-type littermates. n = 6 per group. Scale bar, 25 µm.