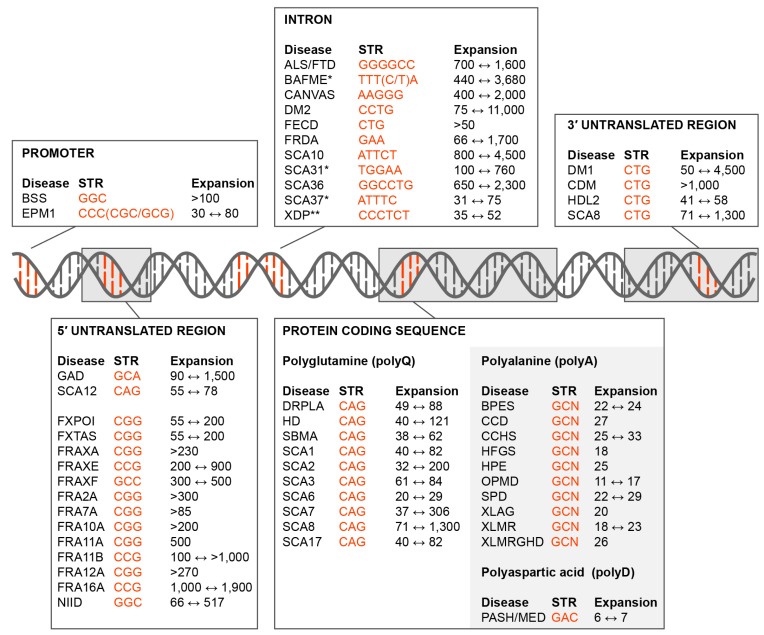
Figure 1.
Short tandem repeat (STR) expansion disorders. Diseases caused by STR (orange font) expansions in the promoter, 5’ untranslated region (5’UTR), introns, coding region and 3’ untranslated region (3’UTR) are shown together with the disease acronym and pathogenic expansion range (black font). Some of these mutations are not classical expansions but are insertions due to replication/recombination/duplication (Intron, SCA31, SCA37, BAFME, *; Protein Coding Sequence, Polyalanine and Polyaspartic acid, light grey box) or retrotransposon (Intron, XDP, **) events. Disease-associated STR locations include the: • Promoter. Baratela-Scott Syndrome (BSS) linked to XYLT1 gene [6], Progressive Myoclonus Epilepsy (EPM1)–CSTB [7]; • 5’UTR. Glutaminase Deficiency (GAD)–GLS [8]; Spinocerebellar Ataxia (SCA) Type 12 (SCA12)–PPP2R2B [9]; Fragile X-Associated Primary Ovarian Insufficiency (FXPOI), Fragile X-Associated Tremor/Ataxia Syndrome (FXTAS) and Fragile XA Syndrome (FRAXA or FXS)–FMR1 [10,11]; Fragile XE Syndrome (FRAXE)–AFF2 [12]; Fragile XF Syndrome (FRAXF)–TMEM185A [13]; Folate-sensitive fragile sites (FSFS) FRA2A–AFF3 [14]; FSFS FRA7A–ZNF713 [15]; FSFS FRA10A–FRA10AC1 [16]; FSFS FRA11A–C11orf80 [17]; SFSF FRA11B–CBL2 [18]; FSFS FRA12A–DIP2B [19]; SFSF FRA16A–LOC109617027 [20]; Neuronal Intranuclear Inclusion Disease (NIID)–NOTCH2NLC [21]; • Intron. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Dementia (ALS/FTD)–C9orf72 [22,23]; Benign Adult Familial Myoclonic Epilepsy (BAFME)–SAMD12, TNRC6A and RAPGEF2 [24]; Cerebellar Ataxia, Neuropathy, Vestibular Areflexia Syndrome (CANVAS)–RFC1 [25]; Myotonic Dystrophy Type 2 (DM2)–CNBP [26]; Fuchs Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy (FECD)–TCF4 [27]; Friedrich’s Ataxia (FRDA)–FXN [28]; SCA type 10 (SCA10)–ATXN10 [29]; SCA type 31 (SCA31)–BEAN1/TK2 [30]; SCA36–NOP56 [31]; SCA37–DAB1 [32]; X-Linked Dystonia-Parkinsonism (XDP)–TAF1 [33]. • Coding region (polyglutamine). Dentatorubral-Pallidoluysian Atrophy (DRPLA)–ATN1 [34]; Huntington Disease (HD)–HTT [35]; Spinal and Bulbar Muscular Atrophy (SBMA)–AR [36]; SCA type 1 (SCA1)–ATXN1 [37], SCA type 2 (SCA2)–ATXN2 [38]; SCA type 3 (SCA3)–ATXN3 [39]; SCA type 6 (SCA6)–CACNA1A [40]; SCA type 7 (SCA7)–ATXN7 [41]; SCA type 8 (SCA8)–ATXN8 [42]; SCA type 17 (SCA17)–TBP [43]; • Coding region (polyalanine). Blepharophimosis Syndrome (BPES)–FOXL2 [44]; Cleidocranial Dysplasia (CCD)–RUNX2 [45]; Congenital Central Hypoventilation Syndrome (CCHS)–PHOX2B [46]; Hand-Foot-Genital Syndrome (HFGS)–HOXA13 [47]; Holoprosencephaly (HPE)–ZIC2 [48]; Oculopharyngeal Muscular Dystrophy (OPMD)–PABPN1 [49]; Synpolydactyly Syndrome (SPD)–HOXD3 [50]; X-linked Mental Retardation and Abnormal Genitalia (XLAG) and X-linked Mental Retardation (XLMR)–ARX [51,52]; XLMR and Growth Hormone Deficit (XLMRGHD)–SOX3 [53]; • Coding region (polyaspartic acid). Pseudoachondroplasia and Multiple Epiphyseal Dysplasia (PSACH/MED)–COMP [54]. • 3’UTR. Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 (DM1) and Congenital Myotonic Dystrophy (CDM)–DMPK [55]; Huntington Disease-Like 2 (HDL2)–JPH3 [56]; SCA8–ATXN8OS [42].