Figure 2.
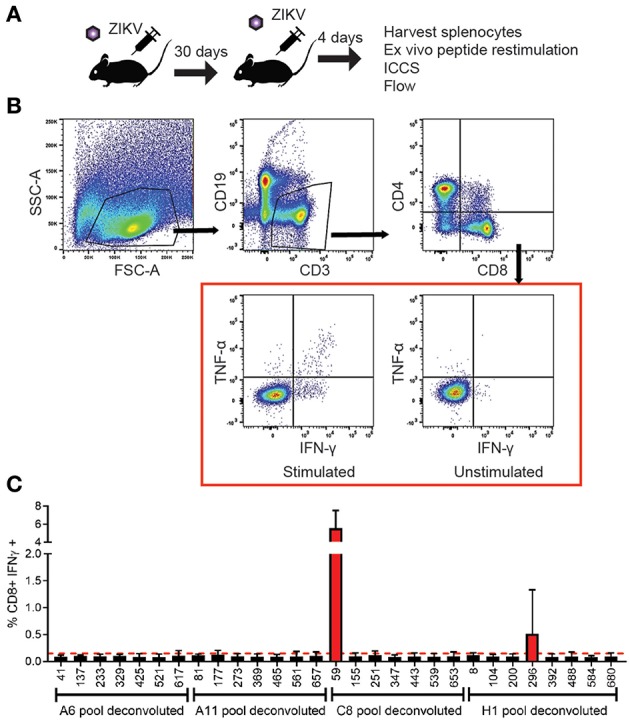
Identification and functional analysis of ZIKV-specific CD8+ T cell epitopes. (A) Diagram of C57BL/6J mice infected 105FFU of ZIKV IV, rested for 30 days then boosted with a second ZIKV infection again with 105 FFU of virus IV. Spleens were harvested 4 days after the boost. The splenocytes isolated from the ZIKV boosted animals were then used in the intracellular cytokine assay. Peptide pools were then used to identify the antigen experienced CD8+ T cells using an intracellular cytokine assay. (B) Representative gating strategy used to analyze intracellularly with antibodies specific for the mouse cytokines interferon-γ (IFN-γ) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). Splenocytes were harvested and stimulated with peptide pools in the presence of brefeldin A. Cells were stained for surface markers (CD3, CD19, CD4, and CD8), stained intracellularly for IFNγ and TNFα and analyzed by flow cytometry. Cells were gated using a lymphocyte gate, CD19−, CD4−, CD8+, and were functionally analyzed by expression of IFNγ. Data is presented as the percent of CD8+ T cells that produced IFNγ in response to pooled peptide stimulation. (C) Peptide pools from wells C8 and H11 from the individual were deconvoluted and the cytokine responses detected from the individual 15mer peptides from the library allowed us to identify 2 possible CD8+ T cell epitopes from the deconvoluted peptide pools. The 15mer peptide epitope was considered positive if the results were two times over background unstimulated samples. The 15mer peptide found in well 59 of the peptide library mapped to and area overlapping between PrM and E was identified from the C8 pool, and a 15mer peptide found in well 196 of the peptide library mapped to NS2b was identified from the H1 pool.
