Figure 3.
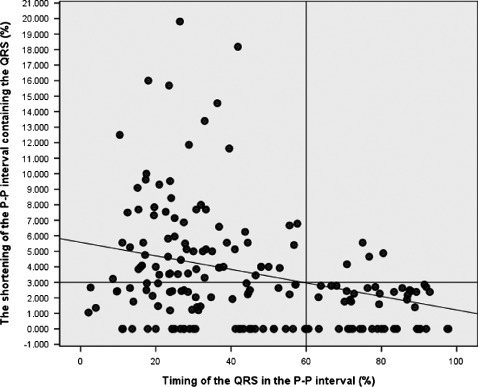
The shortening of the P‐P interval containing a QRS vs the timing of the interposed QRS. P‐P shortening ≤3% occurs randomly, whereas shortening more than 3% is seen predominantly when the QRS occurs in the first 60% of the anticipated P‐P interval. See text for details.
