Figure 2.
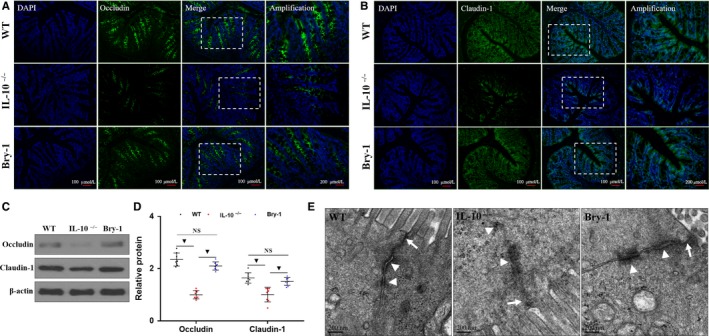
Bryostatin‐1 treated Il‐10 −/− mice showed improved disruption of intestinal mucosal epithelial tight junction proteins than the untreated Il‐10 −/− mice. Intestinal mucosal epithelial tight junction (TJ) protein (green, occludin and claudin‐1) and DAPI staining (blue), merged TJ protein and DAPI staining as well as amplified merged TJ protein and DAPI staining images are presented (A and B). Western blot analysis showed that the expression of claudin‐1 and occludin in the intestinal mucosa was increased significantly in Bry‐1‐treated Il‐10 −/− mice compared with untreated Il‐10 −/− mice, and the expression in the Bry‐1‐treated mice was similar to that in WT mice (C and D). The ultrastructural morphology of the TJ structures of intestinal villi was damaged in Il‐10 −/− mice, and the damaged was characterized by decreased amounts of electron‐dense materials in the TJs (E, white arrows) and abnormal desmosomes (E, white arrowheads). These damaged TJ structures were improved in Bry‐1‐treated Il‐10 −/− mice. Bry‐1, Bryostatin‐1; WT, wild‐type; TJ, tight junction; and NS, no significance. At least three independent experiments with six to eight mice in each group were performed, with one representative experiment is shown. The data are expressed as the mean ± SD. ▼ P < 0.05
