Figure 1.
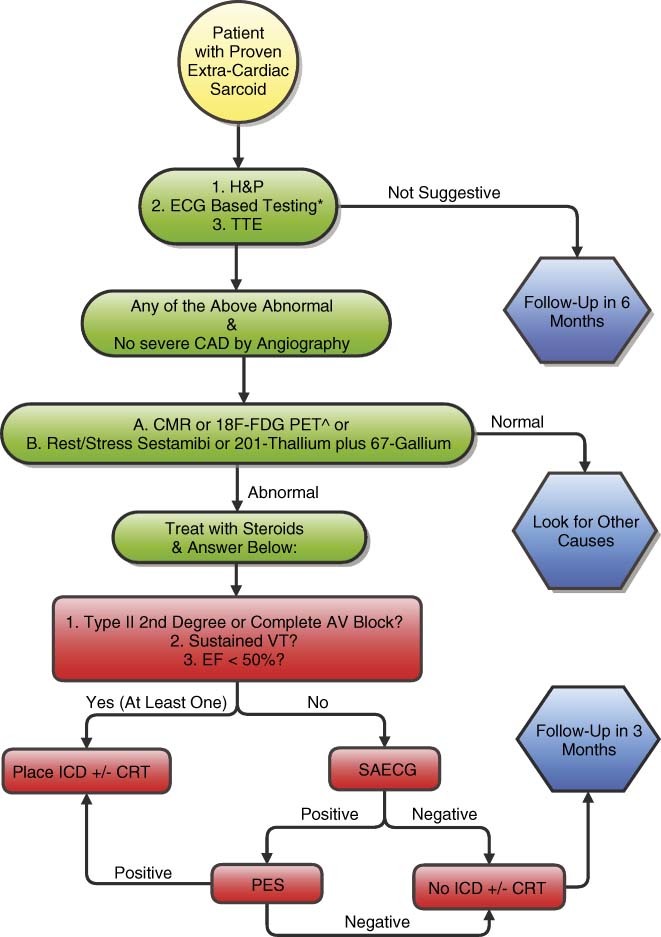
Diagnostic and treatment algorithm for a patient with extracardiac sarcoid. *Abnormal ECG includes: VT (monomorphic or polymorphic) or Mobitz type II or complete heart block on 12‐lead, >100 PVCs on 24‐hour Holter, T wave alternans. Group A: CMR or 18F‐FDG PET are the preferred imaging modalities. They are the most sensitive and specific tests available for cardiac sarcoid. Abbreviations: AV, atrioventricular; CAD, coronary artery disease; CMR, cardiac magnetic resonance; CRT, cardiac resynchronization therapy; ECG, electrocardiogram; EF, ejection fraction; FDG PET, fludeoxyglucose positron‐emission tomography; H&P, history and physical; ICD, implantable cardioverter‐defibrillator; PES; programmed electrical stimulation; PVCs, premature ventricular complexes; SAECG, signal‐averaged electrocardiogram; TTE, transthoracic echocardiogram; VT, ventricular tachycardia.
