FIG 2.
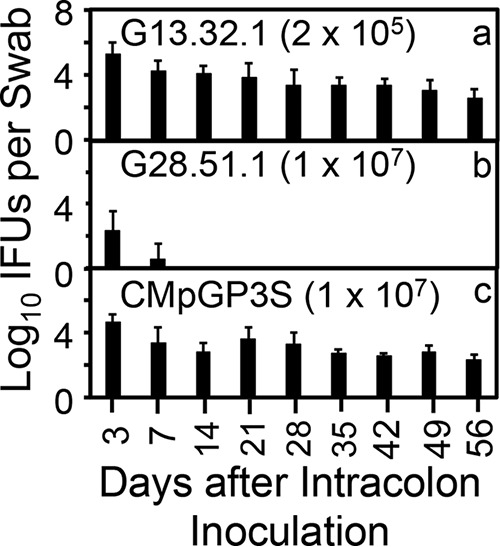
Comparison of C. muridarum with or without mutations in chromosomal genes tc0668 and tc0237 or plasmid gene pgp3 for the ability to colonize the mouse gastrointestinal tract following an intracolonic inoculation. C. muridarum without (G13.32.1) or with mutations in chromosomal genes tc0668 and tc0237 (G28.51.1) or plasmid gene pgp3 (CMpGP3S) was used to infect groups of C57BL/6J mice (n = 5) via intracolon inoculation. On days 3 and 7 and weekly thereafter, after the intracolon inoculation, rectal swabs were taken for monitoring live chlamydial organism shedding. Note that intracolonic inoculation fully rescued the plasmid gene mutant CMpGP3S but not the chromosomal gene mutant G28.51.1. P < 0.05 (for the area under curve for panel a versus panel b but not for panel a versus panel c; Wilcoxon test).
