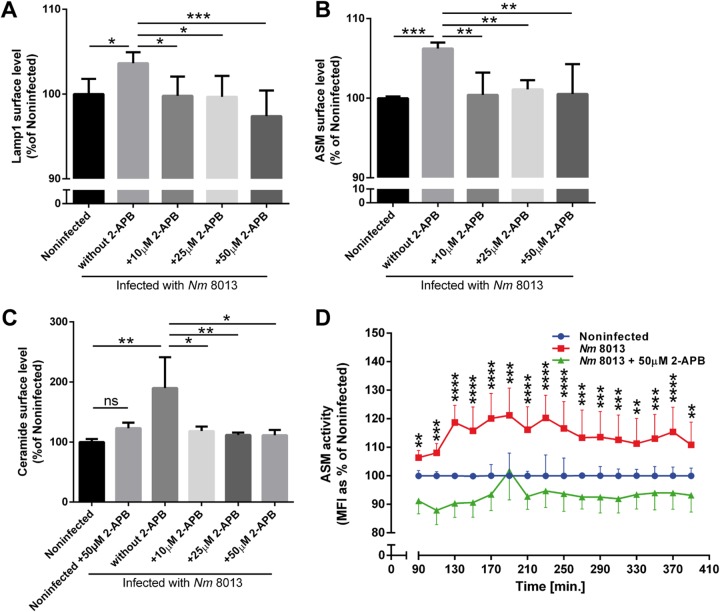
FIG 4.
N. meningitidis-induced ASM translocation to the plasma membrane is Ca2+ dependent. HBMEC were treated with different concentrations of 2-APB (10, 25, 50 μM) for 30 min prior to infection with N. meningitidis 8013. N. meningitidis-induced Lamp1 exocytosis, ASM translocation, and ceramide surface levels were detected by flow cytometry analysis using a mouse IgG PE-conjugated anti-Lamp1 antibody (A), a mouse IgG2a anti-ASM antibody and secondary Cy3-conjugated anti-mouse IgG F(ab′)2 (B), or an anticeramide antibody and secondary Cy5-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgM (C). Data show the mean ± SD levels as a percentage of those for noninfected cells from three independent experiments performed in duplicate. One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test was performed to determine significance. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. (D) ASM activity after infection with bacteria in the presence (50 μM) or absence of 2-ABP. Values show the mean ± SD from three independent experiments. Two-way ANOVA was used to determine significance. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ****, P < 0.0001.