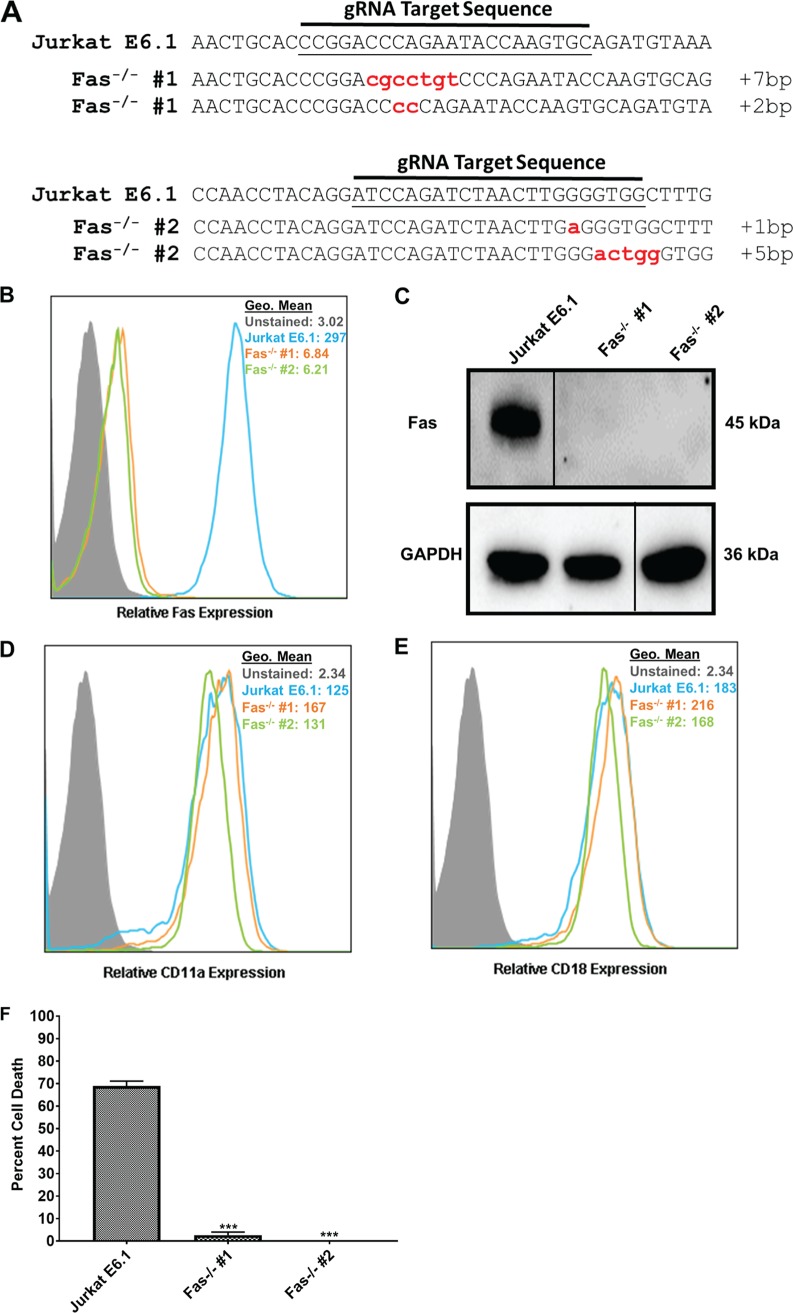
FIG 6.
Characterization of Jurkat Fas knockout cells. (A) DNA from the independent clones with mutations in Fas was isolated, PCR amplified, cloned into a TOPO vector, and sequenced. Sequences were aligned to wild-type Jurkat E6.1 Fas DNA. Any alteration in the DNA sequence was considered gene editing. Each lowercase letter indicates a nucleotide insertion; the number of nucleotides inserted is indicated at the end of each sequence. Sequence of the clone with a deletion in Fas exon 4 (top) and of the clone with a deletion in Fas exon 6 (bottom). (B) Flow cytometric analysis of Jurkat E6.1 cells and both Jurkat Fas−/− clones for surface expression of Fas. Cell populations are indicated according to the legend on the figure. (C) Western blot analysis to confirm deletion of Fas and GAPDH as a loading control. Gels were spliced for labeling purposes. (D and E) Flow cytometric analysis for surface expression of CD11a (D) and CD18 (E) in Jurkat Fas−/− clones. Cell populations are indicated according to the legend on the figure. (F) Jurkat E6.1 cells and Jurkat Fas−/− clones were treated with 10 ng/ml FasL for 24 h, and cell death was assessed via flow cytometry and annexin V/7-AAD staining. Data represent the average of three independent experiments. Error bars represent SEM. The significance of differences between results for Jurkat E6.1 cells and those for each Jurkat Fas−/− clone was determined using Student's t test. ***, P ≤ 0.001.