Figure 6.
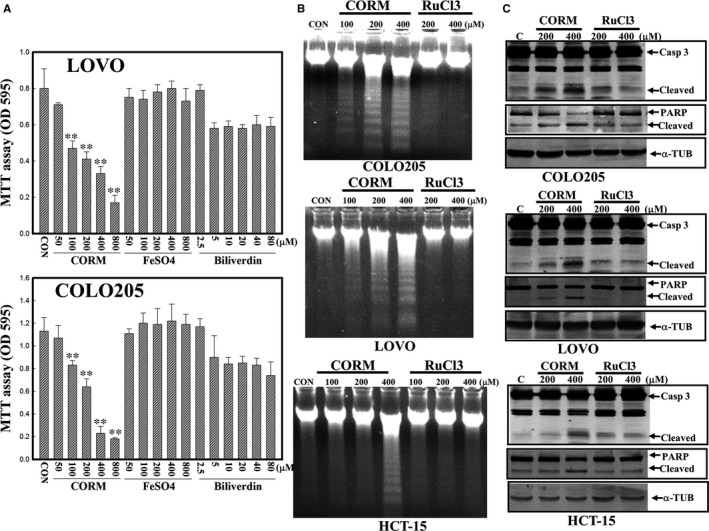
Carbon monoxide (CORM), but not FeSO4 or biliverdin (BV), caused a decrease in the viability of LOVO, HCT‐15 and COLO205 human colorectal carcinoma cells. (A), Both LOVO and COLO205 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of CORM, FeSO4, or BV for 12 h, and the viability of cells was examined by an MTT assay. (B), CORM (RuCO) but not RuCl3 induced DNA ladders in human colorectal carcinoma cells. Cells were treated with indicated concentrations of CORM or RuCl3 for 12 h, and DNA integrity was examined by agarose electrophoresis. (C), CORM, but not RuCl3, induced cleavage in caspase‐3 and poly(ADP) ribose polymerase (PARP) proteins in LOVO, HCT‐15 and COLO205 cells. As described in (B), cleavage of the caspase‐3 and PARP proteins was examined by Western blotting. Data from three independent experiments were obtained, and results are shown as the mean ± SD. **P < 0.01 denotes a significant difference from the control (CON) group
