Figure 5.
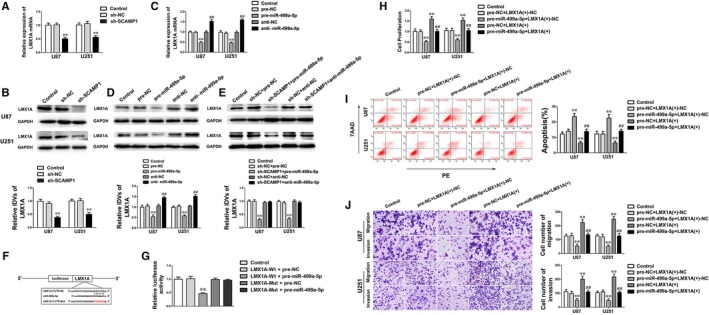
LMX1A was a target of miR‐499a‐5p and rescued the tumour inhibitory effects of miR‐499a‐5p. (A‐B) qRT‐PCR and Western blot assay were used to detect the LMX1A expression after SCAMP1 knockdown. (C‐D) qRT‐PCR and Western blot assay were used to examine the LMX1A expression of U87 and U251 cells after altered miR‐499a‐5p expression. (E) Western blot assay was used to detect the LMX1A expression of U87 and U251 cells co‐transfected with SCAMP1 and miR‐499a‐5p. (F) The potential miR‐499a‐5p binding sites in LMX1A‐3′‐UTR and the designed mutant sequence are indicated. (G) Relative luciferase activity was detected after cells were co‐transfected with pre‐miR‐499a‐5p and LMX1A‐Wt or LMX1A‐Mut. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 3, each group). **P < 0.01 vs LMX1A‐Wt + pre‐NC group. (H‐J) The malignant biological behaviours of U87 and U251 cells co‐transfected with miR‐499a‐5p and LMX1A were detected by CCK‐8 assay, flow cytometry analysis and transwell assay. Scale bars in transwell assay represent 40 μm. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 3, each group). **P < 0.01 vs pre‐NC + LMX1A (+)‐NC group, ## P < 0.01 vs pre‐miR‐499a‐5p + LMX1A (+)‐NC group
