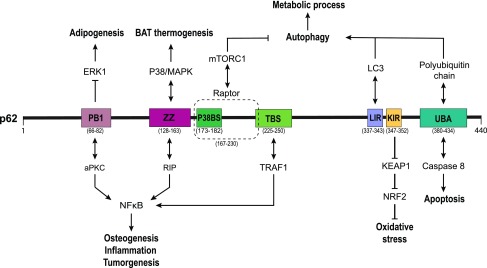
FIG. 1.
The structural domain organization, interacting partners, and functions of p62. p62 is a multidomain protein with roles in the regulation of numerous signaling pathways through distinct binding partners. Depicted are the N-terminal PB1 domain, followed by the ZZ domain, the p38-binding sequence, the TRAF6 binding sequence, LIR, KIR, and a C-terminal UBA domain. aPKC, atypical protein kinase C; BAT, brown adipose tissue; ERK1, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1; Keap1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; KIR, Keap1-interacting region; LC3, microtubule-associated protein light chain 3; LIR, LC3-interacting region; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; mTORC1, mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; NRF2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; p62, p62/SQSTM1; PB1, Phox/Bem1p; RIP, receptor-interacting protein; TBS, TRAF6-binding sequence; TRAF6, tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6; UBA, ubiquitin associated; ZZ, ZZ-type zinc finger. Color images are available online.