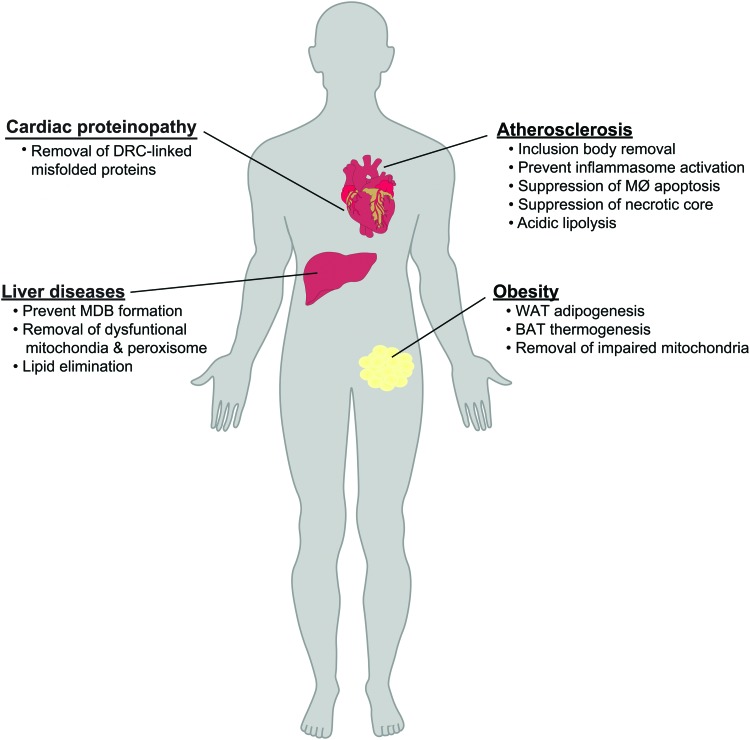
FIG. 4.
Roles for p62 in cardiometabolic diseases. The ability of p62 to mediate distinct autophagic processes implicates it in a variety of cardiometabolic diseases. In atherosclerosis, p62-dependent aggrephagy and removal of inclusion bodies ameliorates atherosclerosis by suppressing macrophage inflammasome activation, apoptosis, and necrotic core formation. In the cardiac proteinopathy, p62-linked autophagy can mediate aggresome formation for removing the DRC-linked proteins. In the liver, p62-dependent aggrephagy prevents accumulation of cytotoxic MDBs) and p62-dependent mitophagy/pexophagy prevents accumulation of dysfunctional mitochondria and peroxisomes, which together ameliorate the progression of fatty liver disease. In obesity, p62-dependent mitophagy modulates WAT adipogenesis, BAT thermogenesis, and the progression of obesity. DRC, desmin-related cardiomyopathy; MDB, Mallory–Denk body; WAT, white adipose tissue. Color images are available online.