Fig. 4.
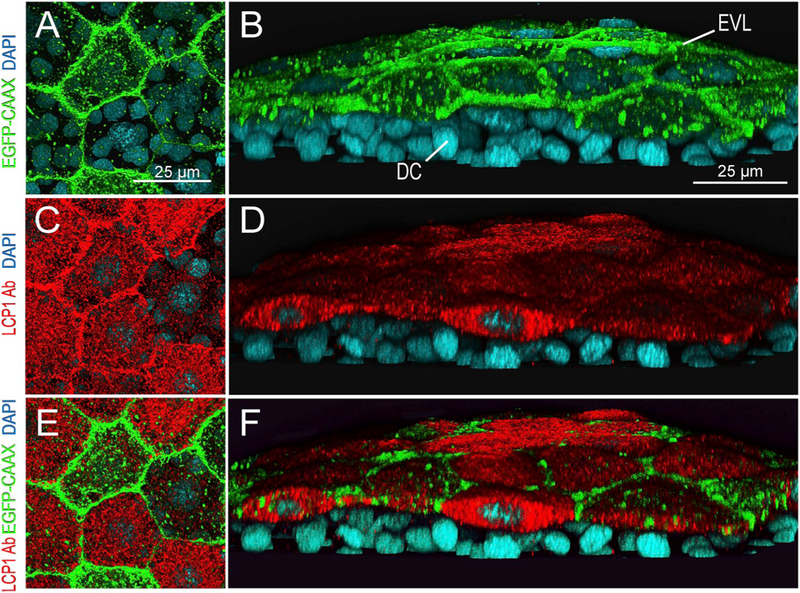
lcp1:EGFP-CAAX and endogenous LCP1 protein co-label the EVL in transgenic embryos.
A. Z-projection showing EGFP signals in EVL cells of a lcp1 :EGFP-CAAX gastrulating embryo. Signals are strongest in the membrane, with scattered foci in cytoplasmic vesicles and perinuclear Golgi.
B. Tilted stack of the same volume as (A), showing EGFP in the EVL but not in the underlying deep cells (DC).
C,D.Red channel views of the same volume, showing whole-mount immunostaining with anti-zebrafish L-plastin. Stain intensity is variegated, but is limited to the EVL.
E. Merged image of A and C.
F. Merged image of B and D. As expected, the two labels are in different compartments: transgenic EGFP-CAAX highlights the EVL membrane, while endogenous L-plastin (an actin-bundling protein) fills the EVL cytoplasm. Neither signal appears in the deep cells.
