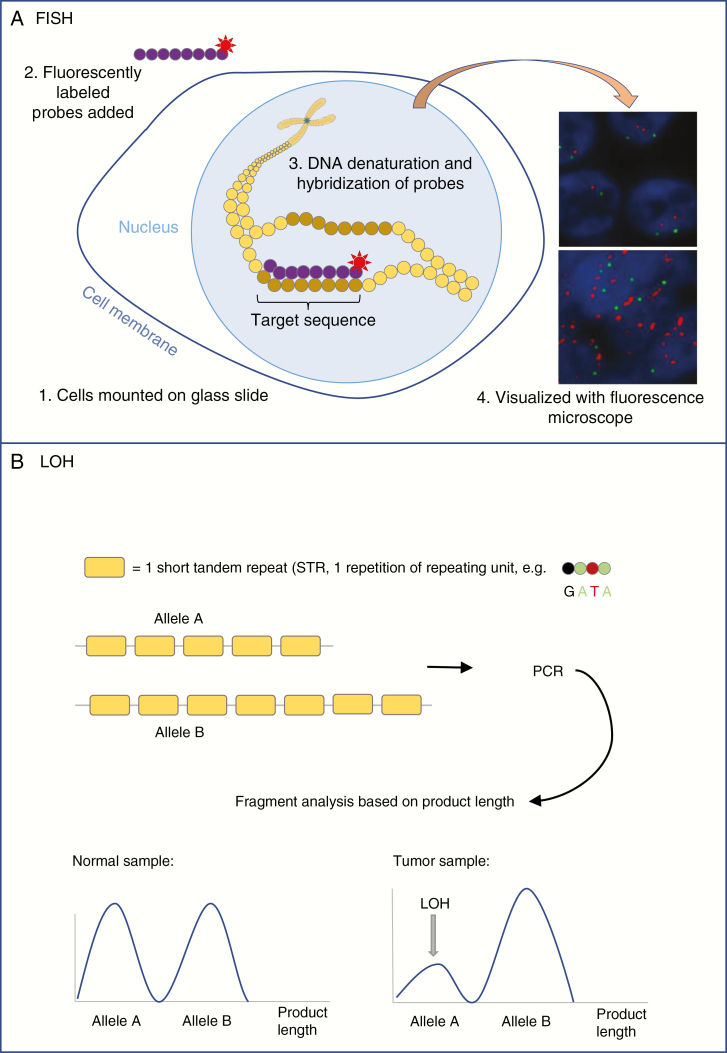
Fig. 3.
A, Simplified diagram showing the essential technique of fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH). Tissue is mounted on a glass slide and cells are treated to make cell membranes and nuclei permeable to enzymes and probes. DNA is denatured and fluorescently labeled probes (eg, complementary to target sequence [red label] and centromere [green label]) are hybridized to the DNA. The fluorescent labels can be visualized with a fluorescence microscope. Normal signal for EGFR (upper panel) and EGFR amplification (bottom panel) are shown. B, Simplified diagram showing the basis of STR-based LOH analysis. For a certain gene, allele A carries 5 STRs while allele B carries 7 copies of that STR. Polymerase chain reaction is performed (see Figure 2), after which the fragments are analyzed based on their length. The ratio between fragments of different lengths gives information on the presence or absence of the alleles. LOH is declared when the presence of 1 of the alleles is lower than expected from the matched normal sample, and when the ratio between the signals for fragments of both alleles is disturbed.
EGFR indicates epidermal growth factor receptor; LOH, loss of heterozygosity; STR, short tandem repeat.