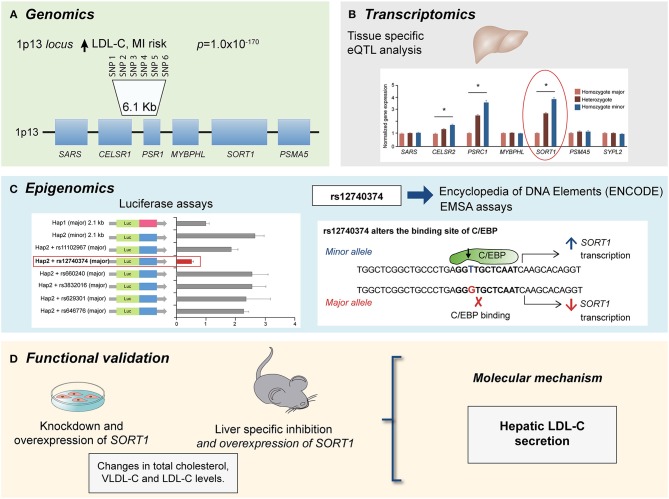
Figure 1.
Multi-omics approach to identify the causal gene associated with LDL-C levels and CAD risk at the 1p13 locus. (A) GWAs meta-analysis showed several SNPs at the 1p13 locus strongly associated with LDL-C levels (p = 1.0 × 10−170) and CAD risk. The 1p13 locus contains several genes (squares). The most significantly associated haplotype for LDL-C comprise six SNPs in high linkage disequilibrium (LD) and is located between CELSR1 and PSR1 genes. (B) Liver eQTL analysis showed the minor haplotype significantly associated with higher expression of CELSR1, PSR1, and SORT1 genes with SORT1 gene showed the largest difference modified from Musunuru et al. (74). (C) By using luciferase assays and ENCODE database it was identified a common polymorphism at the 1p13 locus, rs12740374 that alters the expression of the SORT1 gene in liver with the minor allele (T) creating a C/EBP (CCAAT/enhancer binding protein) transcription factor binding site and the major allele (G) disrupting it. The C/EBP transcriptional factor regulates the expression of hepatic genes involved in metabolism. (D) Functional approaches for SORT1 using small interfering RNA (siRNA) knockdown and viral overexpression in mouse liver showed that SORT1 results in significant changes in plasma LDL-C and very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) particle levels by modulating hepatic VLDL secretion.