Fig. 6. Schematic summarizing how blebbing cells sense and respond to hydraulic resistance.
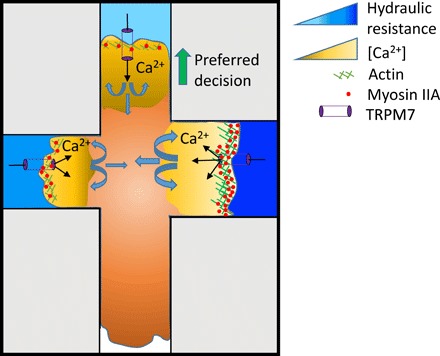
Hydraulic resistance triggers TRPM7 activation in a magnitude-dependent manner, which, in turn, mediates calcium influx and supports a thicker cortical actomyosin meshwork, which preferentially directs cell entrance in low resistance channels. MIIA-GFP signal intensity correlates quantitatively with the hydraulic resistance of each branch channel, whereas the integrated LifeAct-GFP signal intensity correlates inversely with the cell distribution pattern into branches. Variations in bleb size and cortical actin intensity reach a minimum at the decision-making time point, suggesting a physical balance between internal and external cell forces. Inhibition of TRPM7 function or actomyosin contractility alters the decision-making pattern from hydraulic resistance–based to cross-sectional area–based partition.
