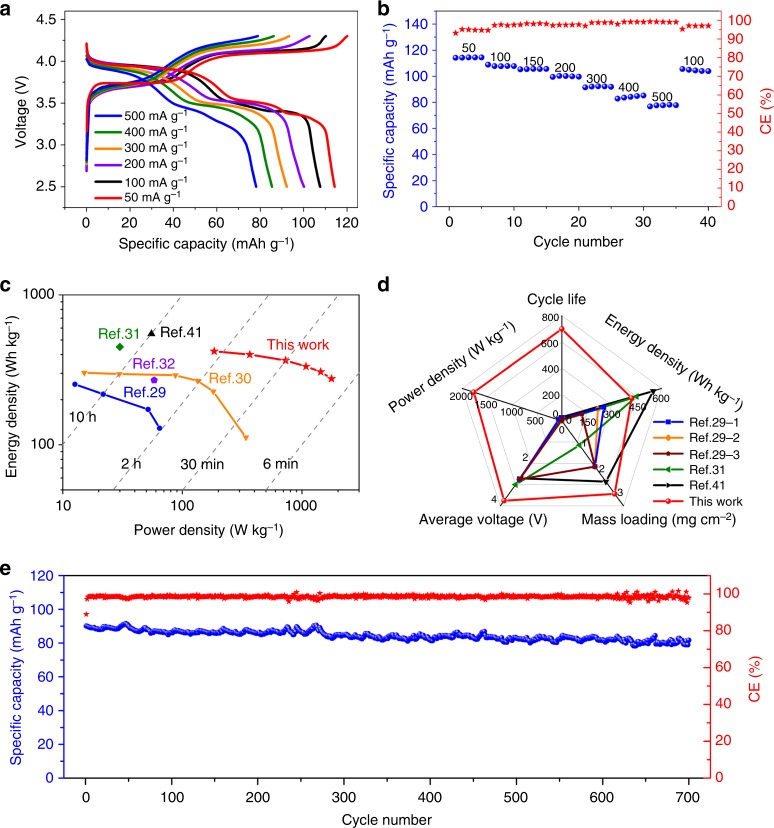
Fig. 4.
Na/NVPF@GO cell performances in buffered Na–Cl–IL electrolyte. a Galvanostatic charge-discharge curves of a Na/NVPF@rGO cell at varied current density from 50 to 500 mA g−1. b Capacity and Coulombic efficiency retention of a Na/NVPF@rGO cell when cycled at different current densities from 50 to 500 mA g−1. c, d Ragone and Radar plots of this work compared with other reported room-temperature Na batteries based on IL electrolytes, respectively29–32,41. The specific capacity, energy and power density in this work and previous literatures were all calculated based on the mass of active materials on positive electrode. The cycle life in (d) is determined by the cycle number when the capacity dropped below 90% of the original capacity29. 1, 2 and 3 represent three different IL electrolytes based on 1 M NaBF4, NaClO4 and NaPF6 salts, respectively. e Cyclic stability of a Na/NVPF@rGO cell using buffered Na–Cl–IL electrolyte at 300 mA g−1