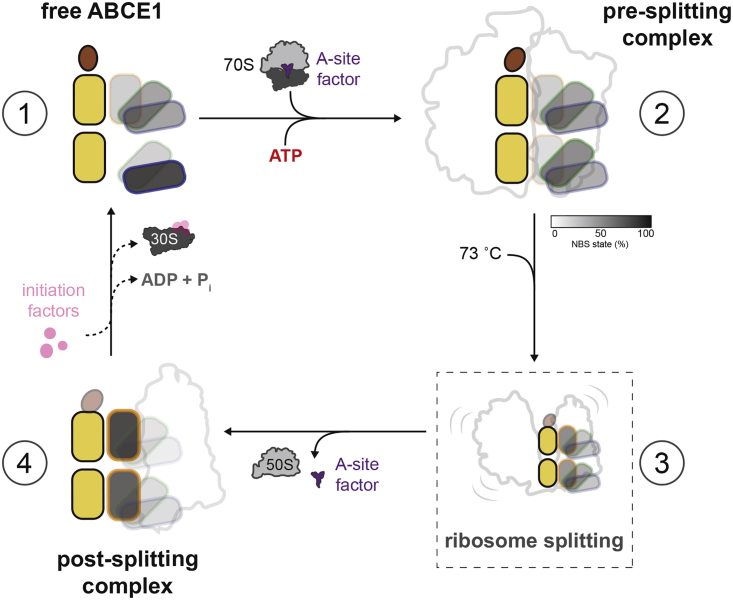
Figure 5.
Dynamics of ABCE1 in Ribosome Recycling
Step 1: free ABCE1 sites are in dynamic equilibrium across three states (open, intermediate, and closed) but predominantly found in the open conformation. ABCE1 displays basal ATPase activity of 5 ATP per minute (see Figure 1D). Step 2: complex with the terminated 70S is mediated by the A-site factors e/aRF1 or e/aPelota and ATP binding. Upon formation of the pre-SC, only site II shifts to the intermediate state, as indicated, and the FeS cluster domain moves toward NBD2 (intermediate; see Figure 2A). Step 3: during splitting, ATP binding and incubation at a physiological temperature trigger the two sites to close, and the FeS cluster domain is repositioned 150° on 30S in the post-SC (closed; see Figures 2A and 2C). Here, either the FeS cluster domain pushes the A-site factor farther into the cleft between the subunits or the domain splits the subunits apart. Step 4: after splitting, bound ABCE1 can build a platform for re-initiation (Heuer et al., 2017). Acquisition of the ADP state triggers dissociation of the post-SC to initiate a new round. ABCE1 is highly dynamic, being at every condition in equilibrium across the indicated conformational states. The percentages of open, intermediate, and closed states for the 2 sites have been experimentally determined for steps 1, 2, and 4. The unstable short-lived step 3 is anticipated to have intermediate values of steps 3 and 4.